Figure 7.
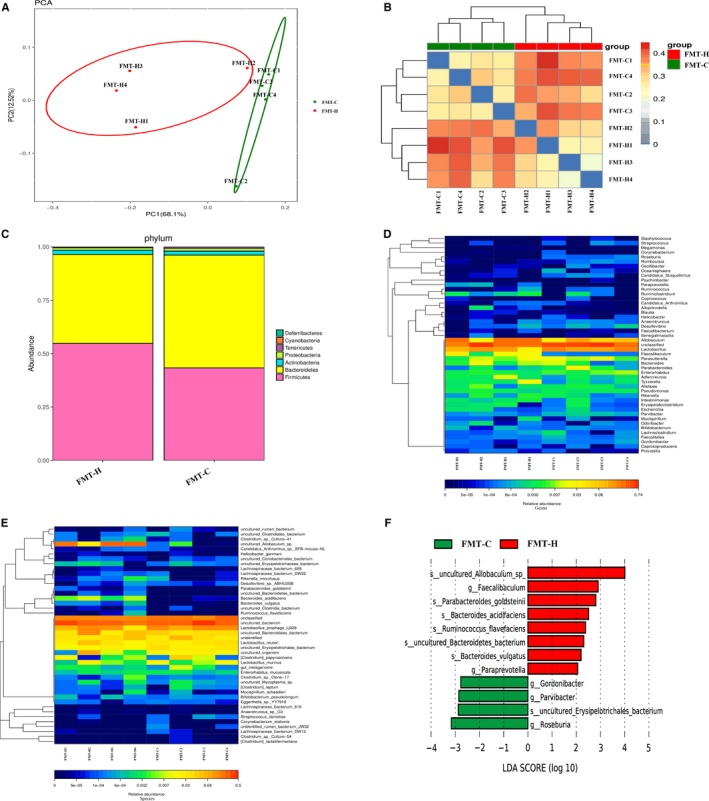
High‐fat diet‐induced dysbiosis could be transmitted to another batch of Apcmin/+ mice. A‐B, Principal component analysis (PCA) and beta‐diversity analysis showed clear difference in faecal microbiota clustering between FMT‐H group and FMT‐C group. C, Differences in microbial community composition between two groups at phylum level. D‐F, Heatmap and LEfSe results showed mice receiving the faecal microbiota from HFD‐fed donors had increased levels of opportunistic pathogens and decreased beneficial bacteria. HFD, high‐fat diet. FMT‐C (transplantation of faecal microbiota from control group to a new batch of recipient Apcmin/+mice). FMT‐H (transplantation of faecal microbiota from HFD group to a new batch of recipient Apcmin/+mice). FMT‐C, n = 4; FMT‐H, n = 4
