Figure 6.
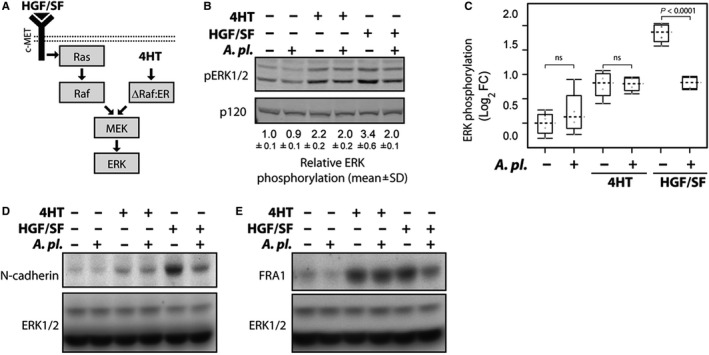
The effect of Arthrospira platensis extract on ERK pathway activation and the expression of N‐cadherin and FRA1 in ΔRaf‐1:ER MDCK cells. A, Schematic representation of ERK activation in response to growth factor HGF/SF or by activation of ΔRaf‐1:ER by 4HT in MDCK cells. HGF/SF (HGF/SF is indicated by a black triangle) and c‐Met signals through Ras to activate Raf‐Mek‐ERK signalling cascade. The right‐hand part illustrates the Ras‐independent, direct activation of the ERK pathway by conditionally active ΔRaf‐1:ER. ΔRaf‐1:ER contains constitutively active domain of Raf‐1 fused to the hormone binding domain of the estrogen receptor (ER). ER holds Raf‐1 protein in the inactive conformation. 4‐hydroxytamoxifen (4HT) induces rapid ΔRaf‐1:ER conversion to active state followed by sustained ERK activation.19 B, A platensis suppresses Ras‐dependent ERK activation. MDCK ΔRaf‐1:ER cells were stimulated with either 4HT (1 μmol/L) or HGF/SF (100 ng/mL) for 8 h. Cell lysates were probed with antibodies recognizing active phosphorylated ERK (pERK1/2) and p120RasGAP. Relative ERK phosphorylation (pERK1/2 signal normalized to p120RasGAP expression from experiment performed in duplicates) is shown below the blot (mean ± SD), with ERK activity in untreated cells as a reference. C, A platensis inhibits ERK phosphorylation in cells stimulated with HGF/SF. Box‐and‐whisker plot showing Log2 fold change in ERK phosphorylation in response to HGF/SF and 4HT. Dashed line indicates median and grey circles individual data point. ns—not significant. D, E, A platensis suppresses the expressions of ERK‐regulated proteins N‐cadherin and FRA1. MDCK ΔRaf‐1:ER cells were stimulated with either 4HT or HGF/SF for 24 h, and lysates were probed with N‐cadherin (panel d) and FRA1 (panel e) antibodies. Equal protein loading was confirmed by blotting for ERK1/2
