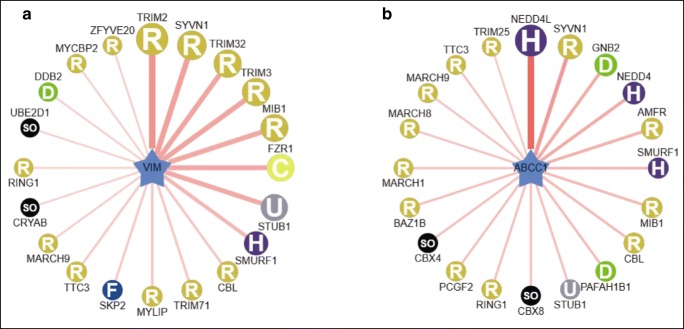
Fig. 8.
Potential upstream mechanisms that cause ubiquitination of vimentin and of MRP1. a Top 20 potential E3s of vimentin. b Top 20 potential E3s of ABCC1. Note: MRP1 is coded by gene ABCC1. The solid line means VIM or ABCC1 directly interacts with its E3-substrates. The line thickness means the interaction intensity. TRIM2 has the highest interaction intensity with vimentin. NEDD4L has the highest interaction intensity with MRP1. H, R, D, U, F, and SO are the subfamilies of E3s. H: HECT (homologous to the E6-AP carboxyl terminus) E3 ligases. R: RING-finger E3 ligases. D: CUL4-DDB1-DWD (Cullin 4-Damaged DNA Binding1-DDB1 binding WD40) E3 ligases. U: U-box E3 ligases. F: F-box E3 ligases. SO: single other E3 ligases such as CRYAB, CKS1B, UBE3C, and BRCC3