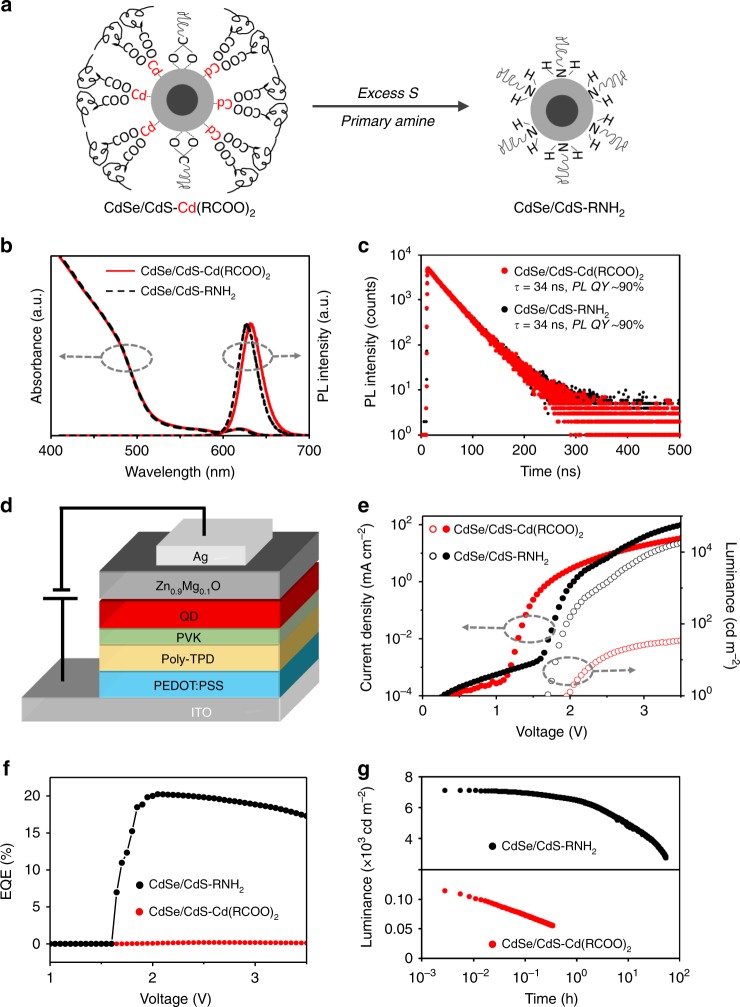
Fig. 1. PL and EL properties of the CdSe/CdS-Cd(RCOO)2 and the CdSe/CdS-RNH2 QDs.
a Ligand exchange from cadmium-carboxylates (with a small amount of negatively charged carboxylates) to primary amines. b Absorption and steady-state photoluminescence (PL) spectra. c Time-resolved PL spectra with mono-exponential PL decay lifetime (τ) and quantum yield (QY). d QLED structure: indium tin oxide (ITO)/ poly(ethylenedioxythiophene):polystyrene sulfonate (PEDOT:PSS, ~35 nm)/poly (N,N9-bis(4-butylphenyl)-N,N9-bis(phenyl)-benzidine) (poly-TPD, ~30 nm)/poly(9-vinlycarbazole) (PVK, ~5 nm)/QDs (~40 nm)/Zn0.9Mg0.1O nanocrystals (~60 nm)/Ag. e Current density and luminance vs. driving voltage characteristics of the QLEDs. f EQE vs. driving voltage characteristics of the QLEDs. g Stability of electroluminescence (EL) of the QLEDs driven at a constant current density of 100 mA cm−2.