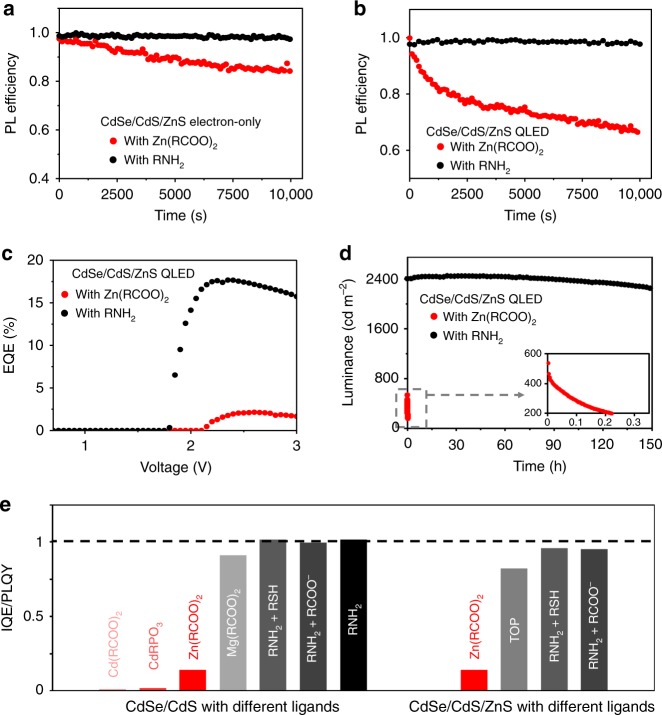
Fig. 4. Electrochemical stability and QLED performance of the red-emitting QDs with different ligands.
a Relative PL efficiency of the CdSe/CdS/ZnS core/shell/shell QDs in electron-only devices (ITO/TPBi (~25 nm)/QDs (~40 nm)/Zn0.9Mg0.1O (~60 nm)/Ag). Zn-carboxylate ligands are less reactive than Cd-carboxylate ones, and thus a constant current density of 100 mA cm−2 is applied for the electron-only devices, instead of 10 mA cm−2 used for the devices with the CdSe/CdS-Cd(RCOO)2 QDs. Inset, the relative PL efficiency of the QDs in hole-only devices (ITO/PEDOT:PSS (~35 nm)/poly-TPD (~30 nm)/PVK (~5 nm)/QDs (~40 nm)/CBP (~25 nm)/MoOx/Au) driven at a constant current density of 30 mA cm−2, sharing the same coordinate axes with the main plot. b, Relative PL efficiency of the CdSe/CdS/ZnS core/shell/shell QDs in QLEDs driven at a constant current density of 100 mA cm−2. c EQE vs. driving voltage characteristics and d, Stability data of the QLEDs based on the CdSe/CdS/ZnS core/shell/shell QDs driven at the constant-current mode. e The IQE/PL QY ratio (IQE of the QLED divided by PL QY of the QD film) for the CdSe/CdS core/shell and the CdSe/CdS/ZnS core/shell/shell QDs with different ligands.