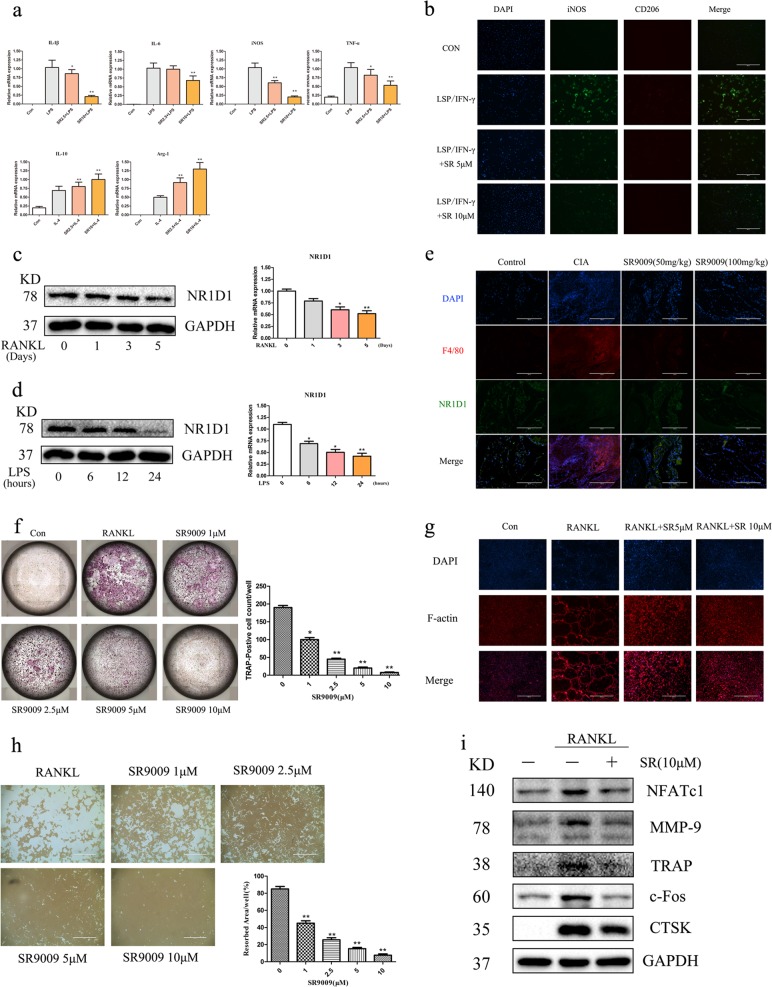
Fig. 6. SR9009 inhibits M1 macrophage polarization and suppresses osteoclastogenesis.
a Real-time PCR showing induction of M1 or M2 markers in BMMs stimulated with LPS (100 ng/mL) + IFN-γ (20 ng/mL) or with IL-4 (20 ng/mL) with or without SR9009. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01 versus cells stimulated with only LPS or IL-4. b BMMs were subjected to immunofluorescence staining with anti-iNOS and anti-CD206 antibodies (original magnification 10×, scale bar = 400 μm). c The expression of NR1D1 during RANKL-induced osteoclastogenesis was analyzed. BMMs were treated with 75 ng/mL RANKL for different periods of time ranging from 0 to 5 days. The expression of the NR1D1 was determined with RT-PCR and Western blot analysis. d The expression of NR1D1 during LPS-induced M1 macrophage was analyzed. BMMs were treated with 100 ng/mL LPS for different periods of time ranging from 0 to 24 h. The expression of the NR1D1 was determined with RT-PCR and Western blot analysis. e Tissue sections were immunohistofluorescence stained with anti-F4/80 and anti-NR1D1 antibodies (left, original magnification 20×, scale bar = 200 μm). f SR9009 inhibits RANKL-induced osteoclastogenesis in a concentration-dependent manner (left). BMMs were seeded in 96-well plates and cultured in complete medium containing 30 ng/mL M-CSF, 75 ng/mL RANKL, and 0, 1, 2.5, 5, or 10 μM SR9009. Trap positive cells with 3 or more nuclei per cell were counted (right). *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01 versus cells stimulated with only RANKL. g SR9009 abolished RANKL-induced F-actin formation. BMMs were seeded onto Osteo-Assay strips, incubated with M-CSF, RANKL, and SR9009 at the indicated concentrations for 6 days, and stained with actin-tracker green and an Alexa-labeled secondary antibody, followed by DAPI. h SR9009 inhibited osteoclast bone resorption (left, original magnification 4×, scale bar = 1000 μm). Osteoclasts were induced on a 0.2% collagen gel-coated six-well plate with RANKL (75 ng/mL) and M-CSF (30 ng/mL) for 6 days, digested, and seeded into Osteo-Assay strip-well plates. Osteoclasts were treated with or without SR9009 for 3 days in the presence of 30 ng/mL M-CSF and 75 ng/mL RANKL. Right panel, densitometric analysis of resorption area from three independent experiments using ImageJ software. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01 versus cells stimulated with only RANKL. i SR9009 suppressed the RANKL-induced expression of NFATc1, MMP9, TRAP, c-Fos, and CTSK. BMMs were cultured with or without 10 mM SR9009 in the presence of M-CSF (30 ng/mL) and RANKL (75 ng/mL).