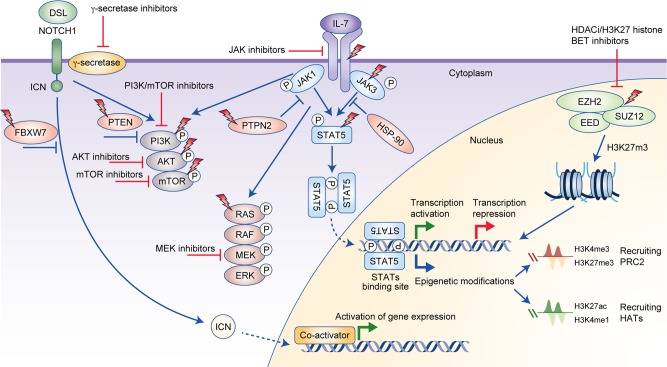
Fig. 2.
Overview of oncogenic pathways activated in T-ALL, the downstream signalling network of interleukin-7 (IL-7), NOTCH1, and polycomb repressor complex 2 (PRC2), and potential therapeutic targets. Binding of cytokine to the IL-7 receptor complex results in dimerisation of the receptor complex, which consequently phosphorylates JAK, as the cytokine receptor itself lacks intrinsic biological activity.50 Activated JAK1 and JAK3 induce phosphorylation of the STAT5 transcription factor, which, following dimerisation, translocates into the nucleus and stimulates gene expression.50 In addition, JAKs activate other downstream signalling cascades including PI3K–mTOR and RAS, which rationalises the use of combinations of inhibitors to promote cell death. STATs can also bind to the enhancer region of genes and modulate the epigenetic status of genes by depositing activating or repressive epigenetic marks through the direct recruitment of PRC2 members, histone acetyltransferases (HATs) or through regulation of their transcription.114 Abnormal NOTCH1 signalling can enhance IL-7R signalling.41 When the NOTCH1 receptor is activated in response to Delta-Serrate-Lag2 (DSL) ligand, signalling is then mediated by intracellular NOTCH1 (ICN), which functions as a transcription factor.115 Translocation of ICN to the nucleus and recruitment of co-activators subsequently activates downstream gene expression.115 Lightning bolts represent the proteins that are mutated in T-ALL. Red proteins are pathway regulators. Potential inhibitors of the proteins and pathways are indicated. BET Bromodomain and Extra-Terminal motif, HAT histone acetyltransferase, HDACi histone deacetylase inhibitor.