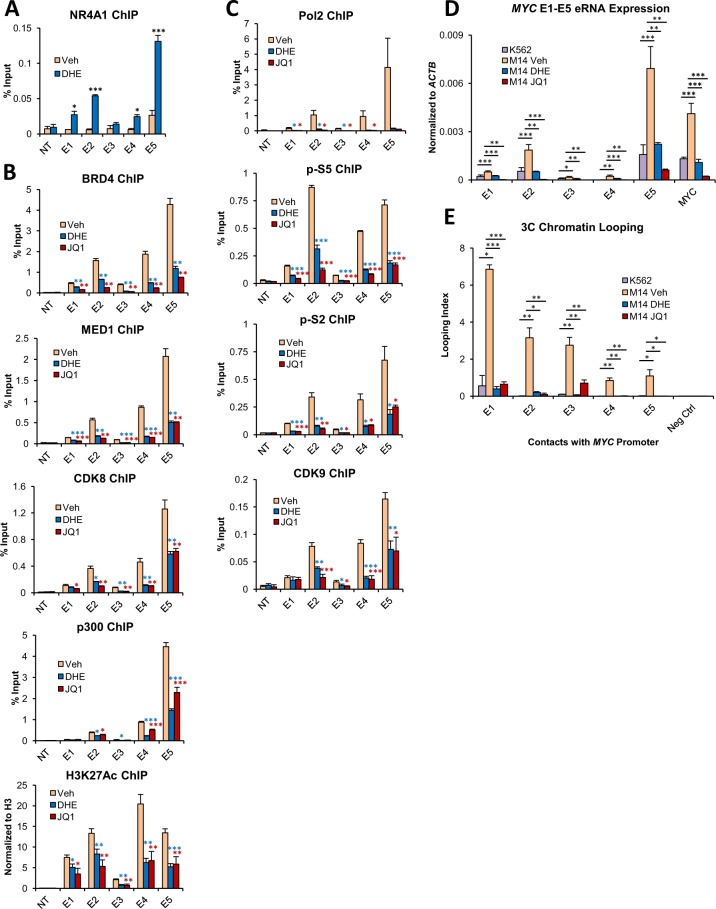
Figure 5.
DHE mimics NR4A-dependent suppression of the MYC SE and displays similar efficacy to BET inhibitor JQ1. MOLM-14 cells were treated with 10 uM DHE or 500 nM JQ1 for 4 hours. (A) ChIP-qPCR for NR4A occupancy at the MYC SE in response to DHE treatment. (B) ChIP-qPCR for BRD4, MED1, CDK8, p300 and H3K27Ac. (C) ChIP-qPCR for total RNA polymerase II (Pol 2), Pol 2 phospho serine 5 (p-S5), Pol 2 phospho serine 2 (p-S2), and CDK9. ChIP-qPCRs for (A–C) were done using primer pairs specific for the MYC SE E1-E5 enhancers. NT represents a non-transcribed gene desert negative control. (D) RT-qPCR for enhancer RNAs (eRNAs) from the MYC SE E1-E5 as well as MYC mRNA in MOLM-14 cells. K562 cells are included as a negative control for eRNA expression at the MYC SE. (E) 3C chromatin looping frequency of interactions between the MYC SE E1-E5 and the MYC promoter. K562 cells are included as a non-looping negative control. Also included is a non-looping negative control genomic region between the MYC locus and the MYC SE. ***p < 0.001, **p < 0.01, *p < 0.05 compared to vehicle or K562 controls.