Figure 2.
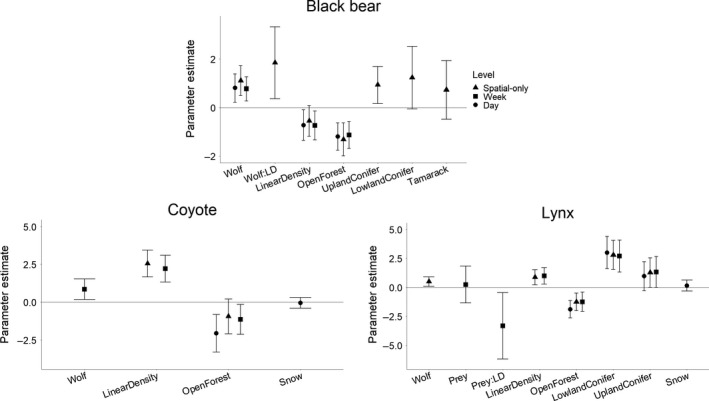
Effects of interspecific interactions and environmental features on predator occurrences. Effect sizes are shown as parameter estimates (mean ± 95% confidence intervals) from negative binomial GLMs (spatial level) and binomial GLMMs (weekly and daily levels) of black bear, coyote, and lynx occurrences at three levels of analysis. Estimates are shown for the most parsimonious model within the top‐ranked models. Estimates have not been back‐transformed, and therefore, values are not directly interpretable in terms of predator occurrences
