Figure 4.
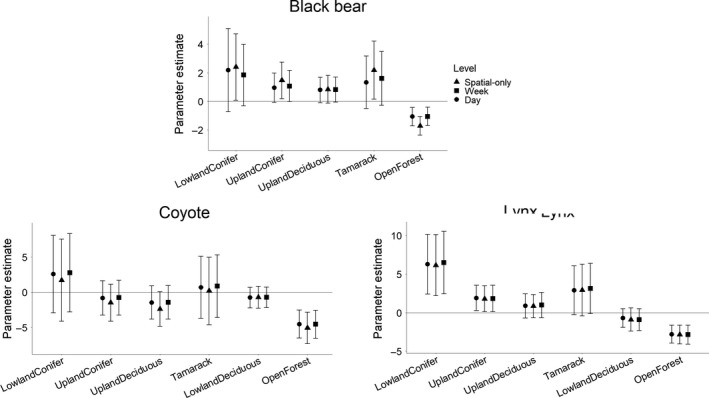
Effects of habitat features on predator occurrences in the habitat modeling step of analysis. Effect sizes are shown as parameter estimates (mean ± 95% confidence intervals) from negative binomial GLMs (spatial level) and binomial GLMMs (weekly and daily levels) of black bear, coyote, and lynx occurrences at three levels of analysis. Results are shown from habitat variables measured at the optimal spatial scale of influence: 250 m for black bears, 1750 m for coyotes, and 1500 m for lynx. Note that LowDecid is absent for black bears because lowland deciduous forest did not occur with 250 m of any camera stations. Significant habitat variables (with confidence intervals that did not overlap zero) were then included in the second step of the analysis to model effects of interspecific interactions on predators
