Figure 2.
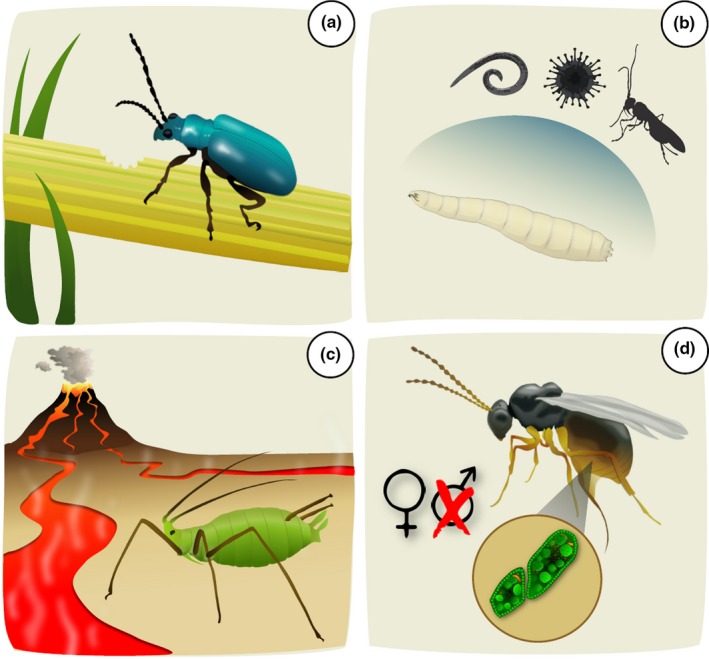
Representative examples of how microbial symbionts influence insect host ecology, physiology, and health. (a) novel symbioses can facilitate host insect feeding on a new food source; (b) the presence of specific microbes can protect a host against natural enemies such as parasitoids, fungi, and nematodes; (c) symbionts can modify host thermal tolerance in both positive and negative ways; and (d) some symbionts, like Wolbachia and Spiroplasma, manipulate host sex ratios by male‐killing, genetic feminization, and by inducing cytoplasmic incompatibility
