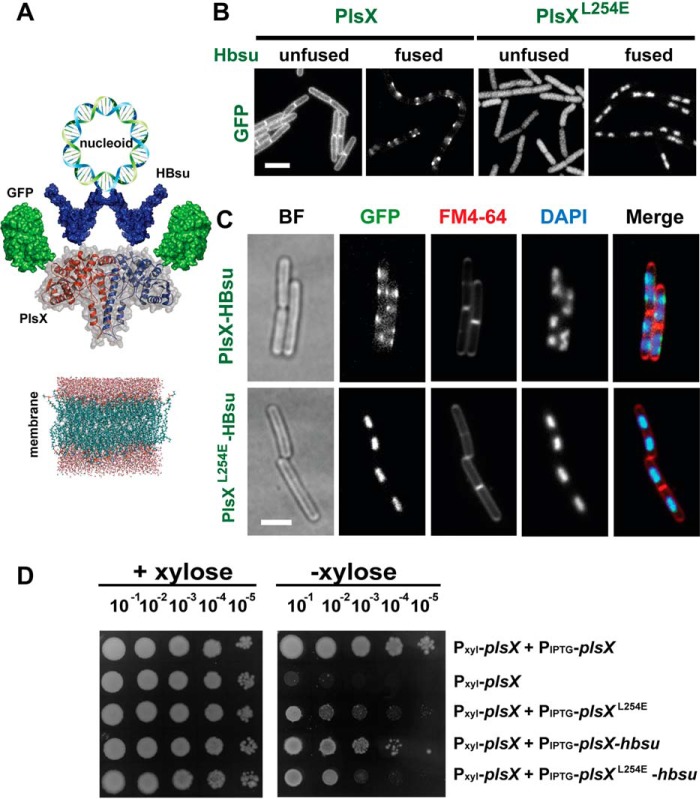
Figure 6.
Subcellular localization of PlsX and PlsXL254E fused to GFP and HBsu. A, schematic representation of the triple fusion GFP-PlsX-HBsu, designed as an attempt to remove PlsX from the cytoplasmic membrane, due to the interaction of HBsu histone-like protein with the nucleoid. B, fluorescence microscopy showing localization of GFP-PlsX wt and GFP-PlsXL254E fused and unfused to Hbsu in B. subtilis strains DS69 (Pxyl-plsX amyE::Physpank-gfp-plsX), DS160 (Pxyl-plsX amyE::Physpank-gfp-plsXL254), DS170 (Pxyl-plsX amyE::Physpank-gfp-plsX-hbsu), and DS171 (Pxyl-plsX amyE::Physpank-gfp-plsX L254E-hbsu). C, fluorescence microscopy showing subcellular localization of GFP-PlsX-HBsu fusions in B. subtilis DS170 (Pxyl-plsX amyE::Physpank-gfp-plsX-hbsu) and DS171 (Pxyl-plsX amyE::Physpank-gfp-plsX L254E-hbsu) using FM4-64 and DAPI to stain membrane and nucleoid, respectively. Images are representative of at least 100 cells analyzed for each condition in at least two different days. All images are at the same magnification. Scale bar = 5 μm. D, growth complementation assays of strains expressing PlsX-HBsu fusions. Cells of DS28 (Pxyl-plsX), DS69 (Pxyl-plsX amyE::Physpank-gfp-plsX), DS160 (Pxyl-plsX amyE::Physpank-gfp-plsXL254), DS170 (Pxyl-plsX amyE::Physpank-gfp-plsX-hbsu), and DS171 (Pxyl-plsX amyE::Physpank-gfp-plsXL254E-hbsu) were grown in liquid LB to logarithmic phase, serially diluted and spotted (4 μl) onto LB + 0.5 mm IPTG plates, with or without 0.4% xylose, and incubated at 37 °C for 24 h. Data shown are representative of at least three independent experiments.