FIG 3.
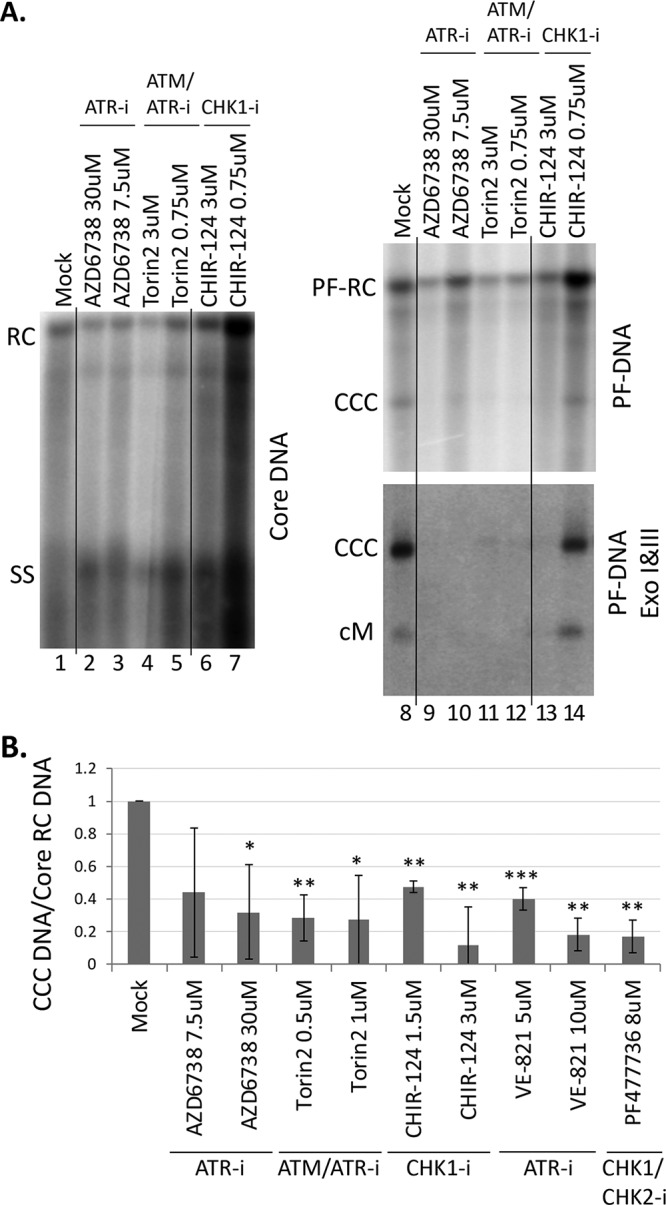
Effects of ATR and CHK1 inhibitors on CCC DNA formation via intracellular amplification in AML12HBV10 cells. HBV replication and CCC DNA formation were induced in AML12HBV10 cells, and the indicated inhibitors were added 4 days after the start of induction. The inhibitors used included the ATM/ATR dual inhibitor Torin2, the ATR inhibitors AZD6738 and VE-821, and the CHK1 inhibitors CHIR-124 and PF477736 at the indicated concentrations. After 3 days of inhibitor treatment (i.e., 7 days of induction), HBV core DNA and PF DNA were extracted from the cells and measured by Southern blotting using a 32P-labeled HBV DNA probe. (A) Representative Southern blot autoradiograms of HBV core DNA (lanes 1 to 7) and PF DNA (lanes 8 to 14, top panel). HBV PF DNA was further treated with Exo I and III to remove RC DNA for specific detection of CCC DNA (lanes 8 to 14, bottom panel). cM, covalently closed minus strand DNA. (B) Quantitative analysis of Southern blot results from multiple independent experiments. The data are expressed as CCC DNA levels normalized to those of core RC DNA, with the normalized CCC DNA level from the mock-treated cells set to 1.0. *, P ≤ 0.05; **, P ≤ 0.01; ***, P ≤ 0.001. The vertical thin lines in the images denote where the different parts of the same gel, and with the same exposure, were spliced together in order to remove other parts of the gel that are not presented here.
