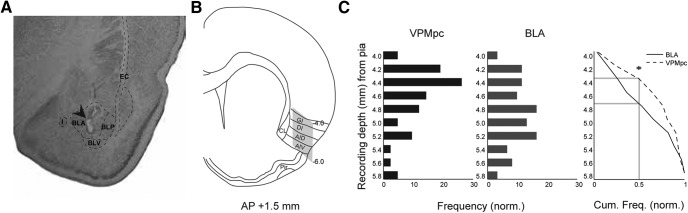
Figure 4.
DV depth profile of GC neurons receiving input from VPMpc or BLA. A, Representative cresyl violet-stained coronal section showing the electrolytic lesion made by the tip of the stimulating electrode in BLA (arrow). BLA, anterior BLA; BLP, posterior BLA; BLV, ventral BLA; I, intercalated nuclei of the amygdala; EC, external capsule. B, Stereotaxic area in which we searched for GC cells for intracellular recording. The craniotomy was centered around AP + 1.5 mm, ML – 5.0 mm from bregma. Gray shading: search area, −4 to −6 mm ventral as measured from the pial surface, sampled with our recordings. Our search area covered all subdivisions of GC. CL., claustrum; GI, granular subdivision; DI, dysgranular subdivision; AID, dorsal agranular subdivision; AIV, ventral agranular subdivision. C, Data were pooled as described in Materials and Methods, and the frequency distribution of cells responding to each stimulation type was plotted against the recording depth of the cell: VPMpc responsive (black bars; n = 42) and BLA responsive (gray bars; n = 61). Right panel, Cumulative sum of frequency comparing cells responding to BLA and VPMpc stimulation. y-axis: recording depth from pia, between −4 and −6 mm; x-axis: frequency. Asterisk indicates KS test p < 0.05.