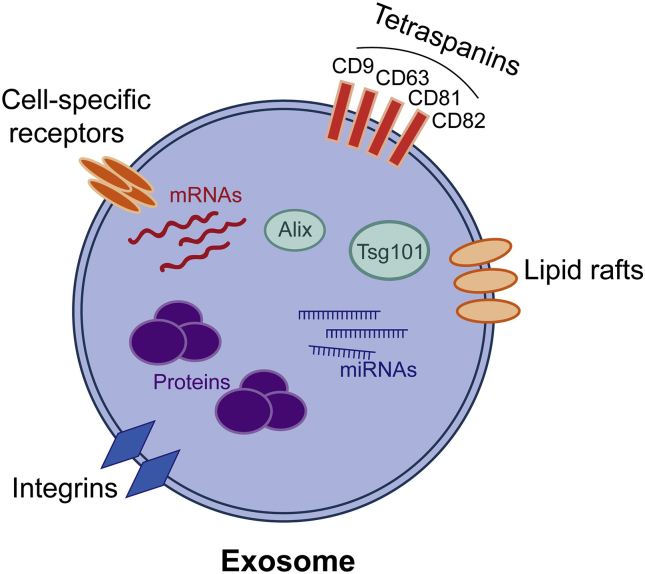
Figure 1.
Diagram of the exosome. Exosomes are membrane-bound extracellular vesicles and have an endosome origin, with a size ranging from 30 nm to 100 nm. Cell-specific receptors, integrins, and lipid rafts can be found in the phospholipid bilayer of the membrane, participating in cell-to-cell communication. Almost all exosomes contain tetraspanins (CD9, CD63, CD81, CD82), multivesicular body biogenesis-related proteins (Alix, Tsg101), heat shock proteins, and some phospholipases. Besides proteins, exosomes also contain mRNAs as well as miRNAs. The composition of exosomes not only reflects the biological state of their parent cells but also affects their functions.