Fig. 2.
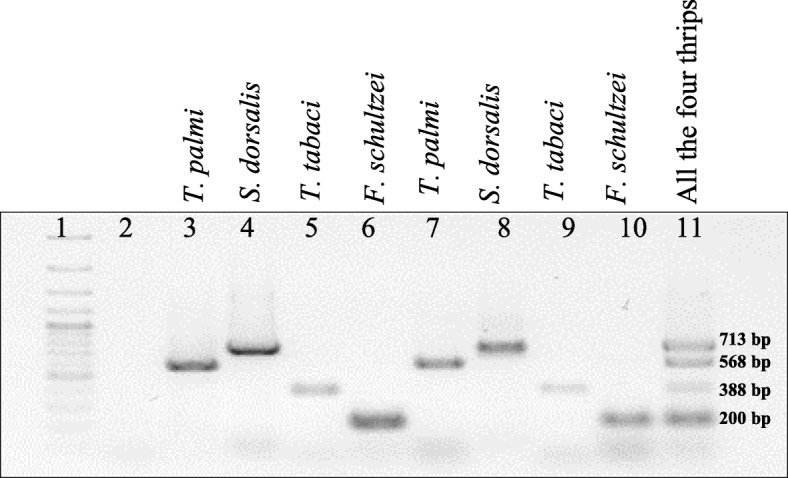
Multiplex PCR assay to identify four thrips vectors concurrently. Multiplex PCR was performed using a cocktail of the four specific-specific primer pairs viz. AG35F-AG36R, AG47F-AG48R, AG87F-AG88R, and AG79F-AG80R for T. palmi, S. dorsalis, T. tabaci, and F. schultzei with the templates of the four thrips vectors separately and mixed templates of all four thrips vectors. Lane 1: 100 bp plus DNA ladder; Lane 2: water control; Lane 3–6: PCR amplicons using species-specific primers with DNA templates of respective thrips vectors, T. palmi (3), S. dorsalis (4), T. tabaci (5), and F. schultzei; Lane 7–11: PCR amplicons using cocktails of primer pairs specific to T. palmi, S. dorsalis, T. tabaci, and F. schultzei with DNA templates of T. palmi (7), S. dorsalis (8), T. tabaci (9), F. schultzei (10), and mixed templates of all four thrips vectors (11). The multiplex PCR using a cocktail of all four thrips vectors amplified products of 568 bp, 713 bp, 388 bp, and 200 bp of T. palmi, S. dorsalis, T. tabaci, and F. schultzei, respectively. The multiplex PCR efficiently discriminated four thrips vectors individually and even in a single reaction when DNA templates of all four thrips vectors were mixed
