Abstract
The epidemiological success of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus USA300 has been associated with the presence of two mobile elements, the arginine catabolic mobile element (ACME) and the copper and mercury resistance (COMER) element. These two mobile elements are associated with resistance to copper, which has been related to host fitness and survival within macrophages. Several studies found that ACME is more prevalent, and exhibits greater diversity, in Staphylococcus epidermidis while COMER has not been identified in S. epidermidis or any other staphylococcal species. We aimed in this study to evaluate the presence and diversity of ACME and COMER-like elements in our S. epidermidis clinical isolates. The genomes of 58 S. epidermidis clinical isolates, collected between 2009 and 2018 in a Scottish hospital, were sequenced. A core-genome phylogenetic tree and genome based MLST typing showed that more than half of the isolates belong to the clinically predominant sequence type2 (ST2) and these isolates have been found to split into two lineages within the phylogenetic tree. Analysis showed the presence of SCCmec in the majority of isolates. Comparative analysis identified a cluster of ACME-positive isolates with most of them belonging to ST48. ACME showed high variation even between isolates of the same ACME type and ST. COMER-like elements have been identified in one of the two major hospital adapted drug resistant ST2 lineages; and showed high stability. This difference in stability at the genomic level correlates well with the up to one hundred times higher excision frequency found for the SCCmec elements in ACME-containing isolates compared to COMER-like element containing isolates. ACME/COMER-like element positive isolates did not show a significant phenotype of decreased copper susceptibility, while resistance to mercury was over-represented in COMER-like element positive isolates. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first molecular characterization of COMER-like elements in S. epidermidis isolates. The presence of the COMER-like elements is the most prominent accessory genome feature of these successful lineages suggesting that this chromosomal island contributes to the success and wide clinical distribution of ST2 S. epidermidis.
Keywords: Staphylococcus epidermidis, mobile genetic element, ACME, COMER, SCCmec
Introduction
Staphylococcus epidermidis and other coagulase negative staphylococci are a leading cause of nosocomial bloodstream and skin and soft tissue infections world-wide (Otto, 2009). Phylogenetic analyses have identified within the species S. epidermidis three major phylogenetic groups of hospital adapted isolates, two of ST2 and one of ST23 (Lee et al., 2018; Méric et al., 2018; Espadinha et al., 2019). The evolutionary pressure of the main nosocomial lineages is thought to be related to the hospital environment, but other evidence suggests that initial core genome changes in sequence type 2 (ST2) isolates result in increased acquisition of resistance traits (Lee et al., 2018). The important role of horizontal gene transfer in the evolution of S. epidermidis (Méric et al., 2018) and the well-established role of Staphylococcus aureus chromosomal cassette elements in bacterial fitness (Purves et al., 2018; Zapotoczna et al., 2018; Rosario-Cruz et al., 2019), suggest that the stepwise evolution of the cassette chromosomal elements and mecA gene is critical to spread of staphylococcal resistance, thus leading to the MRSA and MRSE epidemic (Rolo et al., 2017). The fine balance between acquisition and maintenance of accessory chromosomal elements shapes the evolutionary fitness of S. epidermidis (Zamudio et al., 2019).
The arginine catabolic mobile element (ACME) is a genomic island that first described in Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) clone USA300 North American epidemic (USA300-NAE) and in S. epidermidis ATCC12228 (Diep et al., 2006; Planet et al., 2015). ACME is thought to increase the fitness of staphylococcus species by enhancing their ability to colonize skin and mucous membranes (Diep et al., 2008). ACME shows similar characteristics to the staphylococcal cassette chromosome mec (SCCmec) element in that it integrates into the staphylococcal chromosome at the attachment site attB, which is flanked by direct repeat sequences and is mobilized by the SCCmec encoded ccrAB genes. Moreover, ACME is known to commonly form a composite island with the SCCmec or SCC-associated genes (Diep et al., 2006; Planet et al., 2013; Lindgren et al., 2014; O’Connor et al., 2018a). To date, five distinct ACME types have been described in S. epidermidis; type I harbors the arc and opp3 operons, type II harbors the arc operon only, type III harbors the opp3 operon only, type IV harbors the arc and the kdp operons, and type V harbors all three arc, opp3, and kdp operons. The three characteristic gene clusters; arc, opp3, and kdp encode an arginine deaminase pathway, an oligopeptide permease ABC transporter and potassium ABC transporter respectively. Type IV and V ACME have been identified in oral S. epidermidis only (Diep et al., 2006; O’Connor et al., 2018a, b).
The copper and mercury resistance (COMER) mobile element was described for the first time in S. aureus (MRSA) strain USA300 South American epidemic (USA300-SAE) (Planet et al., 2015). This mobile element located in the USA300-SAE chromosome appears to replace ACME in USA300-NAE adjacent to the SCCmec type IV and it is thought to play a role in COMER which increases fitness as a result of increased survival to copper-mediated killing in macrophages (Planet et al., 2015; Purves et al., 2018; Zapotoczna et al., 2018). The COMER mobile element is associated with an abortive phage infection system and two main gene clusters, the mer operon composed of the merR/A/B genes and the cop operon composed of the copB/L/mco genes (Planet et al., 2015; Purves et al., 2018). To date, the COMER mobile element has not been detected in S. epidermidis strains.
This study investigated the prevalence and evolution of ACME and COMER mobile elements in 58 S. epidermidis clinical isolates retrieved from blood samples. ACME and COMER were detected and characterized using whole genome sequencing (WGS) analysis. This analysis revealed the presence of several variations of ACME as well as detection of previously undescribed COMER-like element in 11 S. epidermidis isolates. The excision and circularization of the ACME and COMER-like elements was investigated.
Materials and Methods
Bacterial Isolates
A collection of 58 S. epidermidis clinical isolates collected between 2009 and 2018 from blood cultures of patients admitted to the ICU of Aberdeen Royal Infirmary (Aberdeen, United Kingdom) were investigated in this study (Table 1). Twenty-five of these isolates were analyzed previously for their biocide resistance gene content (Hijazi et al., 2016). The S. epidermidis strains were stored at −80°C in tryptic soy broth (TSB, BD, France) with 50% glycerol (Thermo Fisher Scientific, United Kingdom). The strains were streaked on tryptic soy agar (TSA) plates (prepared by adding 1.5% agarose to TSB) and incubated at 37°C for 16–24 h. Single colonies were then sub-cultured in TSB and incubated overnight at 37°C/200 rpm in a shaking incubator (Innova 4000, New Brunswick Scientific, United Kingdom).
TABLE 1.
S. epidermidis isolates.
| Isolate | Accession | Date | MLST | COMER-like | ACME | SCCmec type | |
| NB22338Q | STAPH 48 | SAMN12840226 | July 2009 | ST559 | SCCmec-IV | ||
| NB23267V | STAPH 49 | SAMN12840227 | July 2009 | ST2 | COMER | SCCmec-III | |
| NB41003Z | STAPH 51 | SAMN12840228 | May 2010 | ST83 | SCCmec-IV | ||
| NB14428Z | STAPH 53 | SAMN12840229 | May 2010 | ST5 | ACME-V | SCCmec-IV | |
| NB21991B | STAPH 54 | SAMN12840230 | July 2010 | ST5 | SCCmec-IV | ||
| NB24551C | STAPH 56 | SAMN12840231 | August 2010 | ST2 | SCCmec-IV | ||
| NB06465P | STAPH 58 | SAMN12840232 | March 2011 | ST2 | SCCmec-IV | ||
| NB12208Q | STAPH 59 | SAMN12840233 | April 2011 | ST83 | SCCmec-IV | ||
| NB24506S | STAPH 60 | SAMN12840234 | August 2011 | ST2 | COMER | SCCmec-III | |
| NB25777X | STAPH 61 | SAMN12840235 | September 2011 | ST2 | COMER | SCCmec-III | |
| NB26250A | STAPH 62 | SAMN12840236 | September 2011 | ST2 | COMER | SCCmec-III | |
| NB26865Y | STAPH 63 | SAMN12840237 | September 2011 | ST2 | COMER | SCCmec-III | |
| NB28476A | STAPH 64 | SAMN12840238 | October 2011 | ST2 | COMER | SCCmec-III | |
| NB13883R | STAPH 66 | SAMN12840239 | April 2012 | ST19 | |||
| NB25117Z | STAPH 67 | SAMN12840240 | July 2012 | ST210 | |||
| NB25100R | STAPH 68 | SAMN12840241 | July 2012 | ST54 | ACME-I | ||
| NB29474S | STAPH 69 | SAMN12840242 | September 2012 | ST2 | SCCmec-IV | ||
| NB41238E | STAPH 70 | SAMN12840243 | December 2012 | ST2 | SCCmec-IV | ||
| NB01101D | STAPH 73 | SAMN12840244 | January 2013 | ST204 | |||
| NB02243Y | STAPH 74 | SAMN12840245 | January 2013 | ST470 | ACME-IV | ||
| NB03947K | STAPH 75 | SAMN12840246 | January 2013 | ST2 | COMER | SCCmec-III | |
| NB22235H | STAPH 77 | SAMN12840247 | January 2013 | ST59 | SCCmec-IV | ||
| NB26073F | STAPH 78 | SAMN12840248 | July 2013 | ST2 | COMER | SCCmec-III | |
| NB33101Z | STAPH 79 | SAMN12840249 | September 2013 | ST48 | ACME-I | SCCmec-IV | |
| NB671022 | STAPH 83 | SAMN12840250 | February 2014 | ST2 | SCCmec-IV | ||
| NB03169X | STAPH 1 | SAMN12840193 | January 2016 | ST2 | COMER | SCCmec-III | |
| NB03186T | STAPH 2 | SAMN12840194 | January 2016 | ST35 | ACME-I | SCCmec-IV | |
| NB09909V | STAPH 3 | SAMN12840195 | March 2016 | ST48 | ACME-I | SCCmec-IV | |
| NB10503A_1 | STAPH 4 | SAMN12840196 | March 2016 | ST59 | SCCmec-IV | ||
| NB10503A_2 | STAPH 5 | SAMN12840197 | March 2016 | ST5 | SCCmec-IV | ||
| NB11089T | STAPH 6 | SAMN12840198 | March 2016 | ST5 | SCCmec-IV | ||
| NB11582T | STAPH 7 | SAMN12840199 | April 2016 | ST2 | SCCmec-IV | ||
| NB12943Y | STAPH 8 | SAMN12840200 | April 2016 | ST2 | COMER | SCCmec-III | |
| NB13468Z | STAPH 9 | SAMN12840201 | April 2016 | ST23 | SCCmec-IX | ||
| NB13483J | STAPH 10 | SAMN12840202 | April 2016 | ST2 | COMER | SCCmec-III | |
| NB17762B | STAPH 12 | SAMN12840203 | May 2016 | ST528 | ACME-I | ||
| NB18619Q | STAPH 13 | SAMN12840204 | June 2016 | ST2 | SCCmec-IV | ||
| NB20483A | STAPH 14 | SAMN12840205 | June 2016 | ST2 | SCCmec-IV | ||
| NB21362A | STAPH 15 | SAMN12840206 | June 2016 | ST2 | SCCmec-IV | ||
| NB24986M | STAPH 16 | SAMN12840207 | July 2017 | ST54 | ACME-I | SCCmec-IV | |
| NB24987J | STAPH 17 | SAMN12840208 | July 2017 | ST210 | ACME-IV | SCCmec-IV | |
| NB31156H | STAPH 18 | SAMN12840209 | September 2017 | ST65 | |||
| NB31437E | STAPH 19 | SAMN12840210 | September 2017 | ST73 | ACME-II | ||
| NB34495N | STAPH 20 | SAMN12840211 | October 2017 | ST2 | SCCmec-IV | ||
| NB36056Y | STAPH 21 | SAMN12840212 | October 2017 | ST2 | SCCmec-IV | ||
| NB36246W | STAPH 22 | SAMN12840213 | October 2017 | ST210 | ACME-IV | SCCmec-V | |
| NB37325D | STAPH 23 | SAMN12840214 | October 2017 | ST2 | SCCmec-IV | ||
| NB37754V_1 | STAPH 24 | SAMN12840215 | October 2017 | ST2 | SCCmec-IV | ||
| NB37754V_2 | STAPH 25 | SAMN12840216 | October 2017 | ST591 | SCCmec-IV | ||
| NB38801E | STAPH 27 | SAMN12840217 | November 2017 | ST2 | SCCmec-IV | ||
| NB40693L | STAPH 28 | SAMN12840218 | November 2017 | ST2 | SCCmec-IV | ||
| NB41771A | STAPH 29 | SAMN12840219 | November 2017 | ST2 | SCCmec-IV | ||
| NB42838N | STAPH 30 | SAMN12840220 | December 2017 | ST2 | SCCmec-V | ||
| NB43408J | STAPH 31 | SAMN12840221 | December 2017 | ST2 | SCCmec-V | ||
| NB03117S | STAPH 32 | SAMN12840222 | January 2018 | ST2 | SCCmec-IV | ||
| NB03149G | STAPH 33 | SAMN12840223 | January 2018 | ST2 | SCCmec-IV | ||
| NB05012Y | STAPH 34 | SAMN12840224 | January 2018 | ST48 | ACME-I | SCCmec-IV | |
| NB05684Z | STAPH 35 | SAMN12840225 | February 2018 | ST48 | ACME-I | SCCmec-IV |
Whole Genome Sequencing
Genomic DNA extraction was performed using NucleoSpin Tissue Kit (Macherey-Nagel, Germany) following the manufacturer’s instructions. Genomic DNA was eluted in 30 μl pure water, and the concentration and purity measured by the NanoDrop 2000c spectrophotometer (Thermo Fisher Scientific, United Kingdom). Genomic DNA was sequenced on a HiSeq 4000 sequencer (Illumina, The Wellcome Trust Centre for Human Genetics at the University of Oxford) with 150 bp paired-end reads. Genome sequences were trimmed using Trimmomatic (Bolger et al., 2014), then assembled using SPAdes software version v3.9.0 (Nurk et al., 2013) and quality-assessed with QUAST (Gurevich et al., 2013). The draft genomes in contig level for all 58 isolates were submitted to the GenBank under the project number PRJNA574294, the GenBank accession number for the isolates is shown in Table 1.
Multilocus Sequence Typing (MLST) and Core-Genome Phylogeny Tree
The sequence type (ST) of each isolate was specified by submitting the whole genome sequence (WGS) to the S. epidermidis MLST 2.0 online database (Larsen et al., 2012). The core-genome alignment was generated using Roary software version 3.11.2 (Page et al., 2015). Then a maximum likelihood tree for 58 Aberdeen isolates and the BPH0662 reference genome was build using RAxML software version 8.2.X (Stamatakis, 2014). Rstudio v 1.1.4531 and the R package ggtree v 1.13.5 (Yu et al., 2017) was used for visualization and annotation of the phylogeny tree.
Maximum likelihood tree for the 58 Aberdeen isolates and 225 isolates from Lee’s collection (NCBI BioProject numbers: PRJEB12090, PRJNA470534, and PRJNA470752) (Lee et al., 2018) and the BPH0662 reference genome (10.1099/mgen.0.000077) was generated through the iqtree tool (doi: 10.1093/molbev/msu300) by using the Hasegawa–Kishino–Yano model and gamma distribution (Yang, 1994) (10.1007/bf00160154).
Identification of SCCmec, ACME, and COMER-Like Elements
For each isolate, the presence and the type of the SCCmec mobile element was determined by submitting the genome sequence to the SCCmecFinder 1.2 online database (Kaya et al., 2018). Contigs were aligned to the ACME and COMER elements previously characterized in S. aureus USA300 strain FPR3757 (GenBank accession number CP000255) and strain CA12 (GenBank accession number CP007672) respectively using the BLAST software (AltschuP et al., 1990) in order to detect the presence of ACME and COMER elements in the study isolates. In some isolates the ACME and COMER element-associated genes were identified on three and five separate contigs – in this case ACME-I and COMER elements were assembled by PCR. These contigs were organized, reoriented and assembled using BLAST software, Reverse complement tool2 and ISfinder online database (Siguier, 2006). For further investigations, contigs were annotated using the RAST server (Aziz et al., 2008), Artemis sequence viewer (Berriman, 2003) and SnapGene viewer (GSL Biotech)3. This is followed by multiple alignment of the ACME and COMER mobile elements using Mauve software to detect the variation in these elements among the isolates (Darling, 2004).
Metal Susceptibility
The susceptibility of these isolates to several metals including copper sulfate (CuSO4), nickel sulfate (Niso4), iron chloride (FeCl3), manganese sulfate (MnSO4), zinc sulfate (ZnSO4), cobalt bromide (CoBr2), cadmium chloride (CdCL2), mercuric chloride (HgCl2), and sodium arsenate (AsNA2) (all Sigma) was determined using disc diffusion testing. Several colonies from overnight TSA cultures were collected with a sterile loop and re-suspended into Mueller Hinton broth (Oxoid, United Kingdom) to OD600 = 0.5. A Mueller Hinton agar (MHA) plate was seeded with the culture using a sterile swab in three different directions to obtain uniform growth. Ten microliter of 1M solutions of each metal were loaded into a sterile filter discs, obtained from filter papers (Munktell, United Kingdom), and allowed to dry for 15 min. Filter discs were then firmly applied to the surface of the MHA plate and incubated overnight at 37°C. The metal susceptibility was determined using the epidemiological cut-off values (ECOFF) (Morrissey et al., 2014) followed by Fisher’s Exact test to find the susceptibility association among the isolates4. A linear regression model was applied to predict the disk diffusion values based on the presence or absence of the composite element by using the lm function from stats’s R package.
Site-Specific Excision of SCCmec, ACME, and COMER-Like Elements
A qPCR-based method was used to quantify the rate of excision and circularization of the composite SCCmec and ACME/COMER-like elements. Specific primers were designed using SnapGene viewer software (Table 2) and used to amplify the element attachment sites, the circularized SCCmec and SCCmec plus the ACME/COMER-like element and the excision products (chromosome junction after the element excision). Excision of the SCCmec and ACME/COMER-like element was induced in selected isolates using 0.5 μg/ml Mitomycin C (Sigma-Aldrich). qPCR reactions were performed using the TaqMan Fast Advanced Master Mix (Thermo Fisher Scientific) with the following run protocol: initial denaturation step at 95°C for 20 s then 45 cycles of 95°C for 3 s and 60°C for 30 s. The reactions were carried out in MiroAmp Fast 96-Well Reaction Plate (Applied biosystems) using a 7500 real-time PCR machine (Applied Biosystems). The rate of excision was measured using qPCR by comparing the excised circularized element and the reconstituted chromosomal attachment site to the integrated element using this formula: 2–ΔCT (Livak and Schmittgen, 2001).
TABLE 2.
Primers and probes used in the study.
| Primers | Sequence | Annealing temperature (°C) |
| SCCmec-IV AND ACME PRIMERS | ||
| qAttR1 fw | TACGCTCTATCATTCAGCACTATGA | 55 |
| qAttR1 rev | ATGATAAGCTTCTTAAAAACATAACAGC | 55 |
| Probe R1 | CACCAAATGATGCGCGTCATATTGATAGA | 61 |
| qAttR2 fw | AAACCAAAGTCGATATCATCATTTTG | 55 |
| qAttR2 rev | CAGCATTATCGTAAGTTAACTACATT | 55 |
| Probe R2 | CGACTTTAATTATAAAAAACCGCACTCTTAACCG | 61 |
| qAttL fw | GAAGTGATTTTACGATATCACCTTCT | 55 |
| qAttL rev | CATTTAAGATGGAATTCAAATTTTATTTTACTTTC | 54 |
| Probe L | TATATTTCAGTAGGCACCGACGTATACAGAATCA | 61 |
| SCCmec-III AND COMER-LIKE PRIMERS | ||
| qAttR1 fw | CTCTCTTAAATTTTTGTTTGATTAGATTAGACC | 56 |
| qAttR1 rev | ACTTGAAATGAAAGACTGCGG | 56 |
| Probe R1 | ACGCATTCAATATGTCTACACGTGAATTTAGTCT | 62 |
| qAttR2 fw | ACACCAGCTTTCTATGTAGGTAA | 55 |
| qAttR2 rev | ATTTTATTGGAGATACTATATACTTAACCAATTTC | 54 |
| Probe R2 | GCGAAGAAAGCCATTATTATGAGGTGATTGTAG | 61 |
| qAttL fw | GAGCGACAAATTCCAATGTAATAGTA | 55 |
| qAttL rev | ACCAAACAATGAATATATAATACATTTAAGATG | 54 |
| Probe L | GTCGCTCTTTCGTTTCAGTTAAGGAAAATG | 61 |
Results
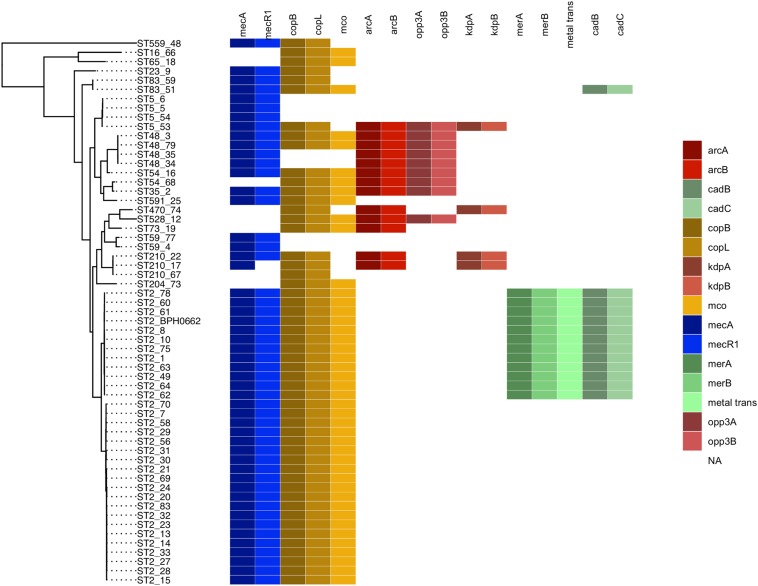
The evolution of S. epidermidis isolates recovered from bloodstream infections between 2009 and 2018 at Aberdeen Royal Infirmary was studied by core-genome phylogenetic analysis (Figure 1). Genome-based MLST revealed that more than 50% of the isolates (31 of 58) belong to the major hospital acquired multidrug resistant ST2 lineage which in turn was found to separate into two sub-lineages as previously described (Lee et al., 2018). The other 16 STs were distributed among different lineages in the phylogenetic tree. Four ST5 isolates, four ST48 isolates and three ST210 isolates. Of the 58 S. epidermidis isolates, 86% (50/58) were methicillin resistant S. epidermidis (MRSE) as they harbored the mecA gene. The vast majority of these MRSE contained SCCmec types III and IV (Table 1). The other eight isolates (14%) considered methicillin sensitive S. epidermidis (MSSE) lacked the mecA gene. All the isolates harbored the penicillin resistance blaZ gene except isolate STAPH74.
FIGURE 1.
Maximum likelihood phylogenetic tree constructed using core genome alignment from the 58 S. epidermidis clinical isolates. The phylogenetic tree is annotated with the isolate’s sequence type ST. Colored boxes to the right of each strain name illustrated the distribution of the SCCmec (blue), cop operon (yellow), ACME (red), and COMER-like element (green) characteristic genes among the S. epidermidis isolates. S. epidermidis BPH0662 used as reference strain in this phylogenetic tree.
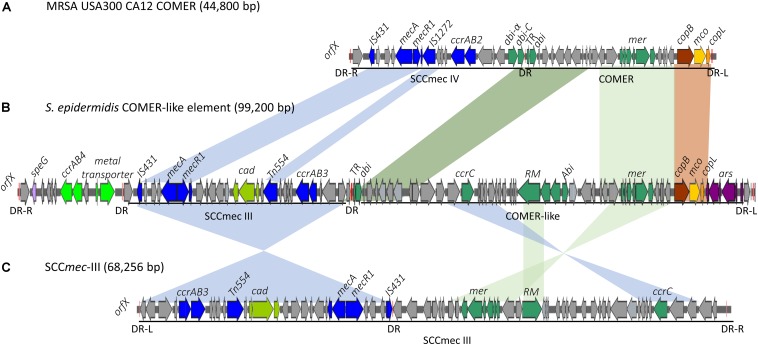
Eleven of the 31 isolates belonging to the clinically predominant ST2 (35%) were found to be positive for a COMER-like element (Figure 1). These eleven isolates were clustered in one of the two ST2 sub-lineages, also containing the reference isolate BPH0662 (10.1099/mgen.0.000077) (Lee et al., 2018). We have named this element COMER-like element as it harbored the mer and cop operons as well as abi gene that exhibited very high nucleotide sequence identity with the mer/cop operons (99.98% identity over 11,028 bp) and abi gene cluster (100% identity over 1,197 bp) located on the COMER element of MRSA USA300 strain CA12 (GenBank accession number CP007672) (Figure 2). However, additional genes not present in COMER USA300, including ars operon and a type I restriction modification system, were identified in the S. epidermidis COMER-like elements. The COMER-like element was found to be a composite island of 99.2 kb in size. The structural organization of this composite island was identical in all eleven isolates with the COMER-like element located immediately downstream of SCCmec-III and encoding the mecA gene and the cad/mer operons with > 99.8% nucleotide sequence identity with the corresponding genes in SCCmec-III of strain 85/2082 (GenBank accession number AB037671). Additionally, this composite island contained a module harboring the speG and ccrAB4 genes and the gene of a putative further metal transporter (locus_tag = ″F9B38_12675) (Figure 2). In contrast to our composite S. epidermidis element, the COMER element in USA300 is located downstream of SCCmec-IV (Figure 2). This is the first description of a COMER-like element in S. epidermidis strains.
FIGURE 2.
Schematic map of the COMER-like elements in S. epidermidis. The COMER element previously described in MRSA USA300 strain CA12 (GenBank accession number CP007672) (A) and the SCCmec-III element previously described in strain 85/2082 (GenBank accession number AB037671) (C) are included for comparison. Characteristic genes of the COMER-like element are colored including the mer operon, the abi genes, and the restriction modification system (green), the cop operon (yellow-brown) and ars operon (purple). The SCCmec element genes colored include the mecA, ccrAB3 genes (blue), and the cad operon (light green). An additional module harboring a metal transporter, ccrAB4 (bright green) and speG genes (light purple) is found upstream SCCmec-III in our S. epidermidis strains (B). Homologous regions between the different elements are shown by shading. The direct repeats (DR) are indicated.
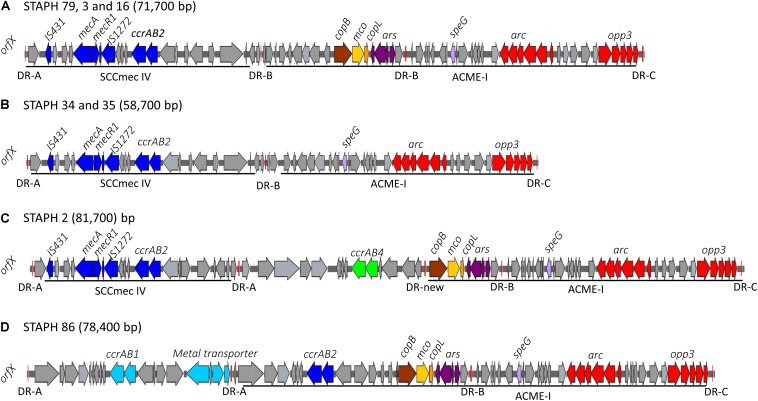
The arginine catabolic mobile element (ACME) was detected in 9/50 (18%) of the MRSE isolates and 4/8 of the MSSE isolates (Figure 1). These ACMEs encoded the arc and/or opp3 and/or kdp operons as previously described for ACME in S. epidermidis (Miragaia et al., 2009; Barbier et al., 2011; Onishi et al., 2013; Soroush et al., 2016; McManus et al., 2017; O’Connor et al., 2018a). The ACME-I element was the predominant ACME type and all ACME-I containing isolates, except isolate STAPH12 (ST528), found to cluster in one lineage in the phylogenetic tree containing ST48, ST54 and ST35. The ACME-I element in these isolates was assembled and found to harbor the arc, opp3 operons, and the speG gene, all flanked by 15 bp direct repeats (DR_B and DR_C). Additionally, one or more modules were found to colocalize with the ACME-I forming a composite island (Figure 3). Comparative analysis tools showed high variability of ACME-I composite island. In 3 out 7 isolates [ST48 (n = 2) and ST54 (n = 1)], the ACME-I was located downstream of the SCCmec-IV, separated by a module composed of ars and cop genes. This module and the SCCmec-IV were flanked by DR_A and B respectively at the 5′end in orfX (Figure 3A). In 2 out of 7 ST48 isolates the ACME-I element colocalized with SCCmec-IV but lacked the ars/cop gene modules (Figure 3B). In one ST35 isolate an additional module harboring the ccrAB4 genes flanked by DR_A and DR_Q was inserted between the ars/cop gene modules and the SCCmec-IV (Figure 3C). The ACME composite island in one ST54 isolate lacked the mecA gene and included only two modules located upstream the ars/cop genes module and the ACME-I. These two modules were flanked by DR_A, _A, and _B respectively at the 5′end in orfX (Figure 3D).
FIGURE 3.
Schematic map of the ACME-I in S. epidermidis. comparative organization of ACME-I composite island in the seven ST48, ST54, ST35 S. epidermidis isolates. The size of each ACME composite island is indicated after the strain names. Four distinct ACME-I composite island were defined according to the additional modules in these elements (A–D). Each gene or group of genes of interest is shaded in color; arc and opp3 operons (red), speG (light purple), copB (brown), mco (light yellow), copL (ornage), ars operon (dark purple), mecA, mecR1, IS431, IS1272, and ccrAB2 (dark blue). The direct repeat (DR) sequences DRA, DR-B, DR-C, and the new DR are indicated.
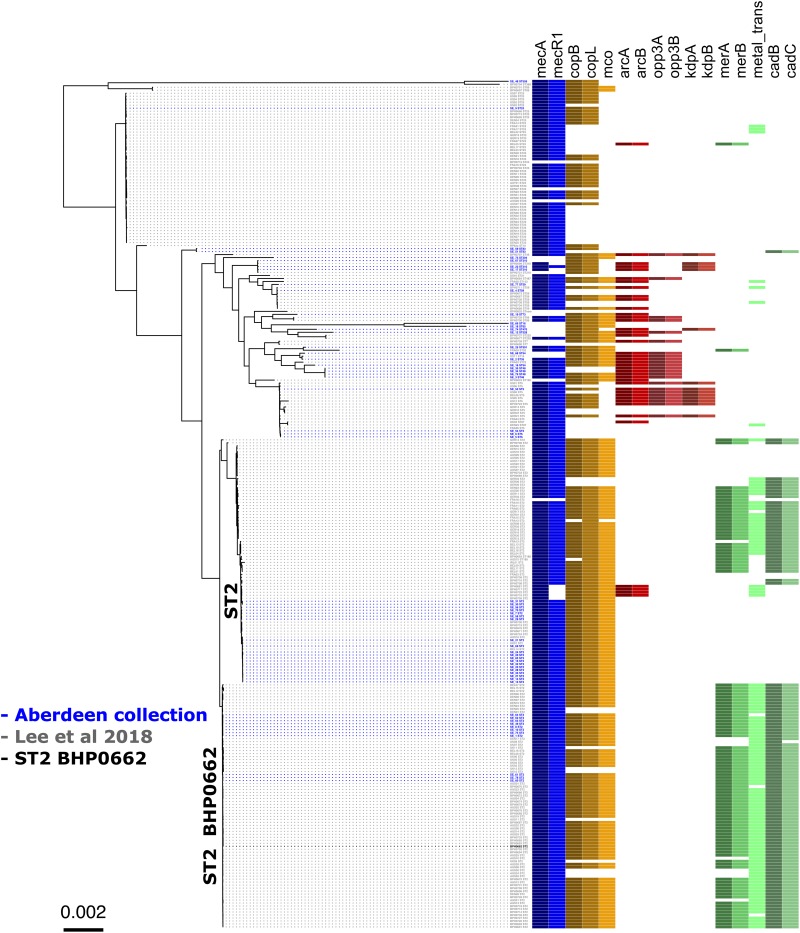
To validate the distribution of the composite SCC elements on a larger dataset and at global level, we generated a core genome phylogenetic tree that included a collection of 225 worldwide S. epidermidis genomes (Lee et al., 2018; Figure 4). The phylogenetic tree was build using the alignment of 1,898 core genes which represent 61.1% (1,706,669 bp) of the reference genome BHP662. This phylogenetic tree combining both datasets showed large clustering of ST2 isolates and their sub-lineages as found in the Scottish collection. Mapping of the key genes of our composite SCC elements, showed again exceptional stability of the COMER-like element. In the larger dataset this element mapped in all 82 isolates belonging ST2 BPH0662 sub-lineage and also partially (38/82) to a second ST2 sub-lineage of ST2 isolates (Figure 4). The mapping in addition confirmed a high variability of ACME elements and their presence in multiple ST and sub-lineages. Copper resistance genes were present in most isolates, even in absence of the COMER-like and ACME elements (Figure 4). As expected nearly all isolates carried SCCmec elements.
FIGURE 4.
Core genome phylogenetic tree of a world-wide collection of S. epidermidis genomes. Maximum likelihood tree of the 58 Scottish isolates (Table 1) (isolates in blue) and the dataset from a world-wide collection of 225 isolates (isolates in gray) (NCBI BioProject numbers: PRJEB12090, PRJNA470534, and PRJNA470752) (Lee et al., 2018). As in Figure 1, the tree is annotated with the isolate’s sequence type (ST) and displays the colored boxes of the heatmap illustrating the distribution of the characteristic genes of the SCCmec (blue), cop operon (brown/yellow), ACME (red) and COMER-like element (green) among the S. epidermidis isolates. Isolate BPH0662 (isolate in black) is used as reference strain in this phylogenetic tree.
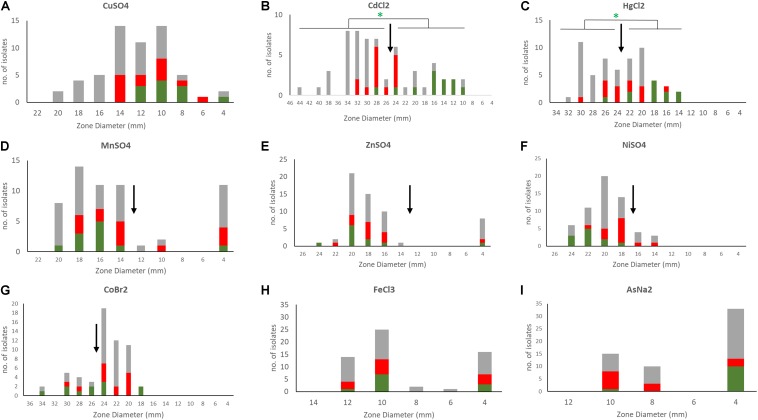
A phenotypic analysis of metal susceptibility of these isolates was performed by disc diffusion susceptibility testing on our Scottish isolates (Figure 5). As no breakpoints for metal resistance exist, we determined the ECOFF (Morrissey et al., 2014). The ECOFF breakpoints, based on the normal distribution of the susceptibility, was defined using the Shapiro–Wilk test. All susceptibility data, except for copper, were not normally distributed. Still we did not define an ECOFF for iron and arsenic as the reduced inhibition zone appears to indicate intrinsic resistance of the all isolates. Isolates belonging to the ST2- BPH0662 lineage carrying the COMER-like element were found to be significantly associated with reduced susceptibility to mercury and cadmium (p < 0.05) using Fisher’s Exact test (Figures 5B,C). The phenotypes match to the presence of the cadmium and mercury transporter in these strains. The linear regression model was applied to predict the disk diffusion value of the cadmium and mercury based on the presence or absence of the COMER-like element in ST2 isolates, the coefficient of correlation for mercury was R2 = 0.57 and for cadmium was R2 = 0.75. No association was found for ACME-carrying isolates.
FIGURE 5.
Susceptibility profiles of S. epidermidis to different metals. Disc diffusion inhibition zones were defined for the 58 S. epidermidis isolates by exposing bacteria to discs containing 10 μl of 1M metal stocks (0.2 M for mercury and arsenic) [(A) copper, (B) cadmium, (C) mercury, (D) manganese, (E) zinc, (F) nickel, (G) cobalt, (H) iron, and (I) arsenic]. Metals tested included copper sulfate (CuSO4), nickel sulfate (Niso4), iron chloride (FeCl3), manganese sulfate (MnSO4), zinc sulfate (ZnSO4), cobalt bromide (CoBr2), cadmium chloride (CdCL2), mercuric chloride (HgCl2), and sodium arsenate (AsNA2). In the bar charts ACME containing isolates are shown in red, COMER-like element containing isolates in green and all other isolates in gray. ECOFFs are shown in arrows. Statistical analysis of the association of isolates carrying COMER-like elements with cadmium and mercury susceptibility is shown (Fisher’s exact test).
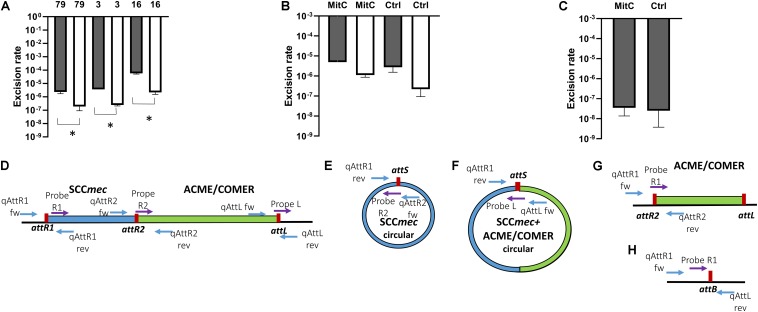
The rate of excision of the composite SCCmec ACME and COMER-like elements was measured by quantitative real time PCR amplification of the reconstituted chromosomal attachment/target site and the circularized elements. Results were compared to the quantification of the integrated elements (considered equivalent to the total quantification of chromosomes). Results for the ACME-I isolates STAPH16, STAPH3, and STAPH79 showed that the SCCmec-IV element alone did excise at a frequency ranging from 5.3 × 10–5 (isolate 16) to 2.7 × 10–6 (isolate 79) (Figure 6A). The excision of the whole composite SCCmec-IV/ACME-I element was significantly lower (1.7 × 10–6 – 1.2 × 10–7) (p < 0.05) using t-test (Figure 6A). The ratio of excision did not significantly change (p > 0.05) in the presence of mitomycin C for any of the isolates, as shown for isolate STAPH79 (Figure 6B). Results for the COMER-like element in isolate STAPH60 showed that the SCCmec-III excised alone at a frequency equal to 2.3 × 10–8 and as with ACME the ratio of excision did not change with mitomycin C induction (Figure 6C). The whole composite SCCmec-III/COMER-like element excision was under the detection limit of our assay. The excision of the SCCmec-III is significantly lower than the SCCmec-IV excision by 100 times (p < 0.05) using t-test.
FIGURE 6.
Excision rates of composite SCCmec elements. The rate of excision was measured using real-time qPCR by comparing the excised circularized element and the reconstituted chromosomal attachment site to the integrated element using this formula: 2–Δ CT. The columns represent the rate of excised element, SCCmec alone (gray) and the composite SCCmec/ACME (white), in isolates STAPH79, STAPH3, and STAPH16. Error bars represent the mean SD of the excised element with and without mitomycin C, asterisk (*) indicates p-value smaller than 0.05 (p < 0.05). (A) Induction with mitomycin C did not affect the excision ratio of the SCCmec (gray) nor the composite SCCmec/ACME (white) in isolate STAPH79 comparing to the control (Ctrl) (B). In STAPH60, like in STAPH79, the mitomycin C induction had no effect on excision frequency with respect to control (Ctrl) (C). The schematic representation of the excision of SCCmec and ACME/COMER-like elements is shown in (D–H) including the chromosome containing the integrated SCCmec (blue) with the ACME/COMER elements (green) (D), the circular form of the SCCmec (E) and circular form SCCmec with ACME/COMER-like element (F), the chromosome with the ACME/COMER element after excision of SCCmec only (G) and the reconstituted chromosome after excision of the whole composite element (H). The att sites are shown in red and the primers used for qPCR are shown as blue arrows and TaqMan probes as purple arrows. The maps are not drawn to scale.
Discussion
In recent decades, S. epidermidis has emerged as a nosocomial pathogen. Genomics showed that the two S. epidermidis hospital-adapted lineages within ST2 are nearly pan-drug resistance (Lee et al., 2018). The evolution of S. epidermidis from commensal to disease-causing bacteria is poorly investigated, although several studies suggested that S. epidermidis acts as a reservoir of resistance genes for S. aureus (Otto, 2009). Comparative genomic analysis of S. epidermidis clinical isolates in this study revealed a high prevalence of methicillin resistance and the MLST showed that more than half the isolates belonged to clinically predominant ST2 confirming the dissemination of this multidrug resistance lineage in our study isolates. The increased capacity of ST2 to acquire drug resistance phenotypes has been attributed to a single polymorphism in the core genome RNA polymerase gene rpoB (Lee et al., 2018). While this original SNP may well be at the origin of the success of ST2, the dominant presence of a large composite COMER-like element in the ST-2 BPH662 lineage is likely very significant to the success of the lineage. The COMER-like element was exceptionally stable when compared to other SCC composite structures, for example ACME (Miragaia et al., 2009; O’Connor et al., 2018b). In S. aureus USA300 the copper resistance phenotype conferred by the COMER element was found to be associated with increased macrophage resistance and fitness (Purves et al., 2018; Zapotoczna et al., 2018). In this study we observed only a mercury and cadmium resistance phenotype only in isolates bearing the COMER-like element, but this may be related to the wide distribution of the copper gene cluster among most S. epidermidis isolates. The role of the additional genes within the COMER-like element, and absent in USA300, in the success of the BPH662 lineage, cannot be inferred at this stage.
This investigation analysing the diversity of composite SCC elements identified, in addition to the well-known ACME elements characterized in S. epidermidis, a highly conserved COMER-like element in one of the main ST2 clusters, the BPH0662-lineage (Zamudio et al., 2019). Different types of ACME identified in this study, including ACME type IV and V, harbored the kdp operon linked previously to oronasal S. epidermidis isolates only (O’Connor et al., 2018b). The findings from oronasal S. epidermidis isolates harboring ACME suggested that each ACME type emerged from the respective identical or closely related ST rather than the site from which the isolates harboring ACME were recovered (O’Connor et al., 2018b). For example, isolates harboring ACME type II and V investigated in this study belonged to ST73 and ST5 respectively, the same STs harboring ACME types II and V in oronasal S. epidermidis. Isolates harboring ACME type I belonged to ST48 as well as ST54 and ST35 (a double locus variant of ST48) and isolates harboring ACME type IV belonged to ST210. However, one isolates with ACME type I and one isolate with ACME type IV belonged to ST528 and a new ST which is closely related to ST470 respectively, suggesting emergence from a different lineage. The variations in the ACME-composite island investigated in this study suggest the rapid evolution of ACME in S. epidermidis. Previous studies of ACME prevalence amongst S. epidermidis populations reported a higher prevalence of ACME in MSSE than MRSE (Miragaia et al., 2009; Barbier et al., 2011; Onishi et al., 2013). Our data are supportive of this finding as ACME was identified in 9/50 (18%) of the MRSE and in 4/8 (50%) of the MSSE.
In addition to confirm excision of the SCCmec elements as previously reported (Stojanov et al., 2015), we report circularization of the ACME element and the S. epidermidis COMER-like element. The excision frequency of the SCCmec-IV in ACME-I containing isolates 16, 3 and 79 ranged from 5.3 × 10–5 to 2.7 × 10–6 while the excision of the composite SCCmec-IV/ACME-I element was approximately 5 times lower. This finding correlates with previous studies on S. aureus in which the rate of excision was estimated to be lower than 10–4 (Ito et al., 1999; Stojanov et al., 2015). Interestingly, the net production of excision products in the presence of mitomycin C did not change for any of the isolates different to what observed previously by others (Liu et al., 2017). The SCCmec-III excision in COMER-like element containing isolate was up to 100 times lower than the SCCmec-IV excision. This shows a strong correlation of excision frequency and genomic variability. We hypothesize that this difference in excision of both the SCCmec and of the composite elements may explain the high genomic stability of the COMER-like elements compared to the high variability of the ACME elements.
Conclusion
In conclusion this work identifies a large composite SCCmec COMER-like element in the main clinical ST-BPH662 lineage of S. epidermidis. The exceptional stability of this large element supports the contribution of this element to the success of this important lineage of clinical S. epidermidis isolates.
Data AvailabiliTy Statement
The datasets generated for this study can be found in the GenBank (accession numbers SAMN12840193–SAMN12840250).
Author Contributions
NA performed the bulk of the laboratory and genomic work, and wrote the manuscript. RZ provided genomic training, contributed high throughput genomic data, and participated in the writing of the manuscript. CJ and CI were involved in phenotypic of clinical isolates and DNA extraction for genome sequencing. JR was involved in genome annotation and DNA extraction. AR was co-supervisor of NA and was involved in data analysis and manuscript preparation. IG supervised the clinical isolate collection and susceptibility testing. JM was co-supervisor of NA and was involved in data analysis and manuscript preparation. KH was involved in planning of the work, data analysis, and manuscript writing. MO conceived and supervised the work and contributed to the writing of the manuscript.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the work of the management team of the ALICE High Performance Computing Facility at the University of Leicester.
Funding. NA was supported by a fellowship of the King Saud University (Riyadh, Saudi Arabia). JR was supported by the BBSRC grant BB/P504737/1.
References
- AltschuP S. F., Gish W., Miller W., Myers E. W., Lipman D. J. (1990). Basic local alignment search tool. J. Microbiol. 215 403–410. 10.1016/S0022-2836(05)80360-2 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aziz R. K., Bartels D., Best A. A., DeJongh M., Disz T., Edwards R. A., et al. (2008). The RAST server: rapid annotations using subsystems technology. BMC Genomics 9:75. 10.1186/1471-2164-9-75 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbier F., Lebeaux D., Hernandez D., Delannoy A.-S., Caro V., François P., et al. (2011). High prevalence of the arginine catabolic mobile element in carriage isolates of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus epidermidis. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 66 29–36. 10.1093/jac/dkq410 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berriman M. (2003). Viewing and annotating sequence data with Artemis. Brief. Bioinform. 4 124–132. 10.1093/bib/4.2.124 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolger A. M., Lohse M., Usadel B. (2014). Trimmomatic: a flexible trimmer for Illumina sequence data. Bioinformatics 30 2114–2120. 10.1093/bioinformatics/btu170 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darling A. C. E. (2004). Mauve: multiple alignment of conserved genomic sequence with rearrangements. Genome Res. 14 1394–1403. 10.1101/gr.2289704 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diep B. A., Gill S. R., Chang R. F., Phan T. H., Chen J. H., Davidson M. G., et al. (2006). Complete genome sequence of USA300, an epidemic clone of community-acquired meticillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Lancet 367:9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diep B. A., Stone G. G., Basuino L., Graber C. J., Miller A., Etages S., et al. (2008). The arginine catabolic mobile element and staphylococcal chromosomal cassette mec linkage: convergence of virulence and resistance in the USA300 clone of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. J. Infect. Dis. 197 1523–1530. 10.1086/587907 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Espadinha D., Sobral R. G., Mendes C. I., Méric G., Sheppard S. K., Carriço J. A., et al. (2019). Distinct phenotypic and genomic signatures underlie contrasting pathogenic potential of Staphylococcus epidermidis clonal lineages. Front. Microbiol. 10:1971. 10.3389/fmicb.2019.01971 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gurevich A., Saveliev V., Vyahhi N., Tesler G. (2013). QUAST: quality assessment tool for genome assemblies. Bioinformatics 29 1072–1075. 10.1093/bioinformatics/btt086 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hijazi K., Mukhopadhya I., An-Bott F., Milne K., Al-Jabri Z. J., Oggioni M. R., et al. (2016). Susceptibility to chlorhexidine amongst multidrug-resistant clinical isolates of Staphylococcus epidermidis from bloodstream infections. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 48 86–90. 10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2016.04.015 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito T., Katayama Y., Hiramatsu K. (1999). Cloning and nucleotide sequence determination of the entire mec DNA of pre-methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus N315. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 43 1449–1458. 10.1128/AAC.43.6.1449 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaya H., Hasman H., Larsen J., Stegger M., Johannesen T. B., Allesøe R. L., et al. (2018). SCC mec finder, a web-based tool for typing of staphylococcal cassette chromosome mec in Staphylococcus aureus using whole-genome sequence data. mSphere 3:e00612-17 10.1128/mSphere.00612-17 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larsen M. V., Cosentino S., Rasmussen S., Friis C., Hasman H., Marvig R. L., et al. (2012). Multilocus sequence typing of total-genome-sequenced bacteria. J. Clin. Microbiol. 50 1355–1361. 10.1128/JCM.06094-11 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee J. Y. H., Monk I. R., Gonçalves da Silva A., Seemann T., Chua K. Y. L., Kearns A., et al. (2018). Global spread of three multidrug-resistant lineages of Staphylococcus epidermidis. Nat. Microbiol. 3 1175–1185. 10.1038/s41564-018-0230-7 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindgren J. K., Thomas V. C., Olson M. E., Chaudhari S. S., Nuxoll A. S., Schaeffer C. R., et al. (2014). Arginine deiminase in Staphylococcus epidermidis functions to augment biofilm maturation through pH homeostasis. J. Bacteriol. 196 2277–2289. 10.1128/JB.00051-14 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu P., Wu Z., Xue H., Zhao X. (2017). Antibiotics trigger initiation of SCCmec transfer by inducing SOS responses. Nucleic Acids Res. 45 3944–3952. 10.1093/nar/gkx153 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Livak K. J., Schmittgen T. D. (2001). Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2−ΔΔCT method. Methods 25 402–408. 10.1006/meth.2001.1262 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McManus B. A., O’Connor A. M., Kinnevey P. M., O’Sullivan M., Polyzois I., Coleman D. C. (2017). First detailed genetic characterization of the structural organization of type III arginine catabolic mobile elements harbored by Staphylococcus epidermidis by using whole-genome sequencing. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 61:e01216-17. 10.1128/AAC.01216-17 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Méric G., Mageiros L., Pensar J., Laabei M., Yahara K., Pascoe B., et al. (2018). Disease-associated genotypes of the commensal skin bacterium Staphylococcus epidermidis. Nat. Commun. 9:5034. 10.1038/s41467-018-07368-7 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miragaia M., de Lencastre H., Perdreau-Remington F., Chambers H. F., Higashi J., Sullam P. M., et al. (2009). Genetic diversity of arginine catabolic mobile element in Staphylococcus epidermidis. PLoS One 4:e7722. 10.1371/journal.pone.0007722 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrissey I., Oggioni M. R., Knight D., Curiao T., Coque T., Kalkanci A., et al. (2014). Evaluation of epidemiological cut-off values indicates that biocide resistant subpopulations are uncommon in natural isolates of clinically-relevant microorganisms. PLoS One 9:e86669. 10.1371/journal.pone.0086669 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nurk S., Bankevich A., Antipov D., Gurevich A. A., Korobeynikov A., Lapidus A., et al. (2013). Assembling single-cell genomes and mini-metagenomes from chimeric MDA products. J. Comput. Biol. 20 714–737. 10.1089/cmb.2013.0084 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O’Connor A. M., McManus B. A., Coleman D. C. (2018a). First description of novel arginine catabolic mobile elements (ACMEs) types IV and V harboring a kdp operon in Staphylococcus epidermidis characterized by whole genome sequencing. Infect. Genet. Evol. 61 60–66. 10.1016/j.meegid.2018.03.012 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O’Connor A. M., McManus B. A., Kinnevey P. M., Brennan G. I., Fleming T. E., Cashin P. J., et al. (2018b). Significant enrichment and diversity of the staphylococcal arginine catabolic mobile element ACME in Staphylococcus epidermidis isolates from subgingival peri-implantitis sites and periodontal pockets. Front. Microbiol. 9:1558. 10.3389/fmicb.2018.01558 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Onishi M., Urushibara N., Kawaguchiya M., Ghosh S., Shinagawa M., Watanabe N., et al. (2013). Prevalence and genetic diversity of arginine catabolic mobile element (ACME) in clinical isolates of coagulase-negative staphylococci: identification of ACME type I variants in Staphylococcus epidermidis. Infect. Genet. Evol. 20 381–388. 10.1016/j.meegid.2013.09.018 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Otto M. (2009). Staphylococcus epidermidis — the “accidental” pathogen. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 7 555–567. 10.1038/nrmicro2182 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Page A. J., Cummins C. A., Hunt M., Wong V. K., Reuter S., Holden M. T. G., et al. (2015). Roary: rapid large-scale prokaryote pan genome analysis. Bioinformatics 31 3691–3693. 10.1093/bioinformatics/btv421 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Planet P. J., Diaz L., Kolokotronis S.-O., Narechania A., Reyes J., Xing G., et al. (2015). Parallel epidemics of community-associated methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus USA300 infection in North and South America. J. Infect. Dis. 212 1874–1882. 10.1093/infdis/jiv320 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Planet P. J., LaRussa S. J., Dana A., Smith H., Xu A., Ryan C., et al. (2013). Emergence of the epidemic methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus strain USA300 coincides with horizontal transfer of the arginine catabolic mobile element and speG-mediated adaptations for survival on skin. mBio 4:e00889-13. 10.1128/mBio.00889-13 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Purves J., Thomas J., Riboldi G. P., Zapotoczna M., Tarrant E., Andrew P. W., et al. (2018). A horizontally gene transferred copper resistance locus confers hyper-resistance to antibacterial copper toxicity and enables survival of community acquired methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus USA300 in macrophages: Staphylococcus aureus copper resistance and innate immunity. Environ. Microbiol. 20 1576–1589. 10.1111/1462-2920.14088 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rolo J., Worning P., Boye Nielsen J., Sobral R., Bowden R., Bouchami O., et al. (2017). Evidence for the evolutionary steps leading to mecA-mediated β-lactam resistance in staphylococci. PLoS Genet. 13:e1006674. 10.1371/journal.pgen.1006674 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosario-Cruz Z., Eletsky A., Daigham N. S., Al-Tameemi H., Swapna G. V. T., Kahn P. C., et al. (2019). The copBL operon protects Staphylococcus aureus from copper toxicity: CopL is an extracellular membrane–associated copper-binding protein. J. Biol. Chem. 294 4027–4044. 10.1074/jbc.RA118.004723 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siguier P. (2006). ISfinder: the reference centre for bacterial insertion sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 34 D32–D36. 10.1093/nar/gkj014 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soroush S., Jabalameli F., Taherikalani M., Amirmozafari N., Imani Fooladi A. A., Asadollahi K., et al. (2016). Investigation of biofilm formation ability, antimicrobial resistance and the staphylococcal cassette chromosome mec patterns of methicillin resistant Staphylococcus epidermidis with different sequence types isolated from children. Microb. Pathog. 93 126–130. 10.1016/j.micpath.2016.01.018 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stamatakis A. (2014). RAxML version 8: a tool for phylogenetic analysis and post-analysis of large phylogenies. Bioinformatics 30 1312–1313. 10.1093/bioinformatics/btu033 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stojanov M., Moreillon P., Sakwinska O. (2015). Excision of staphylococcal cassette chromosome mec in methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus assessed by quantitative PCR. BMC Res Notes 8:828. 10.1186/s13104-015-1815-3 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang Z. (1994). Maximum likelihood phylogenetic estimation from DNA sequences with variable rates over sites: approximate methods. J. Mol. Evol. 39 306–314. 10.1007/BF00160154 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu G., Smith D. K., Zhu H., Guan Y., Lam T. T.-Y. (2017). ggtree: an r package for visualization and annotation of phylogenetic trees with their covariates and other associated data. Methods Ecol. Evol. 8 28–36. 10.1111/2041-210X.12628 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Zamudio R., Oggioni M. R., Gould I. M., Hijazi K. (2019). Time for biocide stewardship? Nat. Microbiol. 4 732–733. 10.1038/s41564-019-0360-6 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zapotoczna M., Riboldi G. P., Moustafa A. M., Dickson E., Narechania A., Morrissey J. A., et al. (2018). Mobile-genetic-element-encoded hypertolerance to copper protects Staphylococcus aureus from killing by host phagocytes. mBio 9:e00550-18. 10.1128/mBio.00550-18 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Data Availability Statement
The datasets generated for this study can be found in the GenBank (accession numbers SAMN12840193–SAMN12840250).