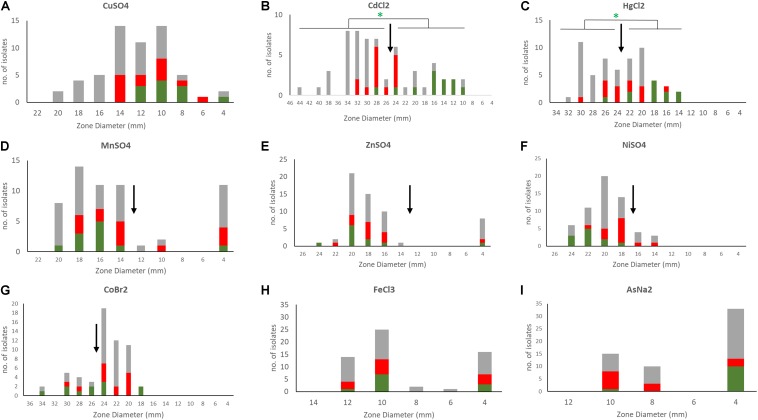
FIGURE 5.
Susceptibility profiles of S. epidermidis to different metals. Disc diffusion inhibition zones were defined for the 58 S. epidermidis isolates by exposing bacteria to discs containing 10 μl of 1M metal stocks (0.2 M for mercury and arsenic) [(A) copper, (B) cadmium, (C) mercury, (D) manganese, (E) zinc, (F) nickel, (G) cobalt, (H) iron, and (I) arsenic]. Metals tested included copper sulfate (CuSO4), nickel sulfate (Niso4), iron chloride (FeCl3), manganese sulfate (MnSO4), zinc sulfate (ZnSO4), cobalt bromide (CoBr2), cadmium chloride (CdCL2), mercuric chloride (HgCl2), and sodium arsenate (AsNA2). In the bar charts ACME containing isolates are shown in red, COMER-like element containing isolates in green and all other isolates in gray. ECOFFs are shown in arrows. Statistical analysis of the association of isolates carrying COMER-like elements with cadmium and mercury susceptibility is shown (Fisher’s exact test).