Figure 5.
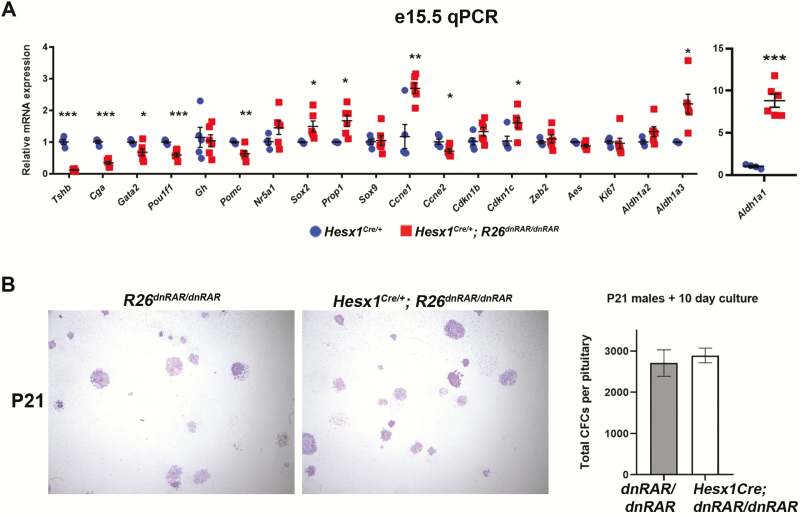
Inhibition of pituitary retinoic acid (RA) signaling upregulates expression of stem cell and transitional markers but does not increase clonogenic potential. A, Quantitative polymerase chain reaction (qPCH) in e15.5 Hesx1Cre/+; R26dnRAR/dnRAR embryos confirms severe downregulation of Tshb seen by immunofluorescence. Other thyrotrope markers such as Cga, Gata2, and Pou1f1 are reduced but to a lesser degree than Tshb. Expression of the melanotrope/corticotrope marker Pomc is also reduced. Expression of the stem cell markers Sox2 and Prop1, as well as cell cycle progression markers Ccne1 and Cdkn1c, are elevated at e15.5 by qPCR, whereas EMT/migration genes Zeb2 and Aes are not. Aldh1a1 and Aldh1a3 are upregulated in the conditional mutant pituitaries. (n = 4 and 6). B, Three-week-old R26dnRAR/dnRAR and Hesx1Cre/+; R26dnRAR/dnRAR male pituitary glands were dispersed and assessed for colony-forming potential after 10 days in culture. No significant differences were noted between genotypes. Conditional mutant stem cells form both densely packed and sparse-flat types of colonies and comparable numbers of colonies per pituitary gland (n = 3 and 3).