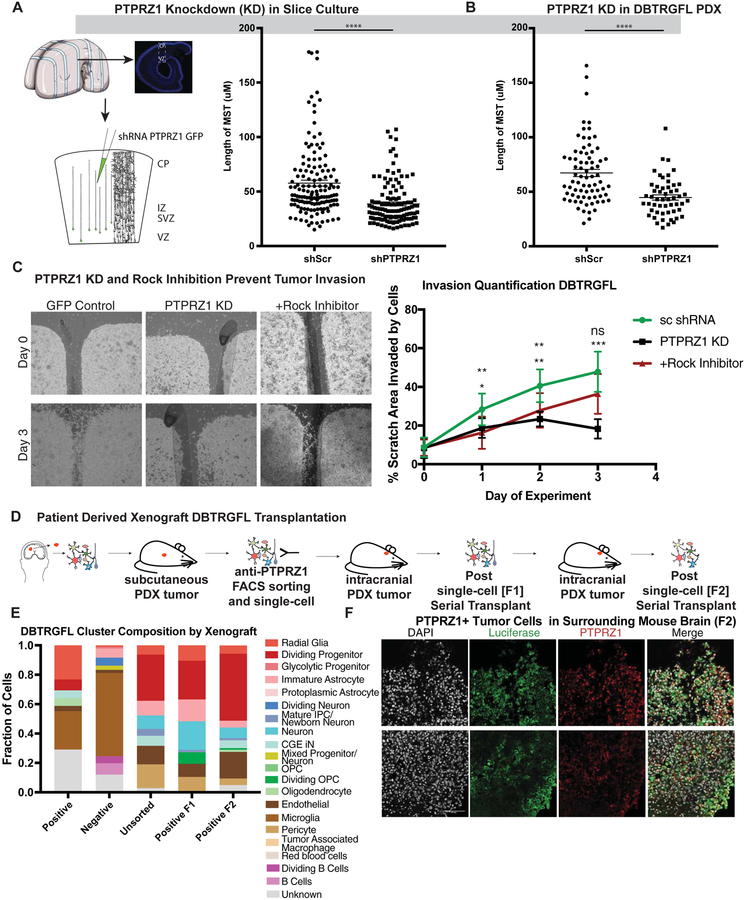
Figure 6. PTPRZ1 Promotes MST driven invasiveness of glioblastoma.
a) Short hairpin induced knockdown of PTPRZ1 (**** = p < 0.0001, Student’s two-sided t-test) decrease the length of somal translocation length using 3 biological replicates and 4 technical replicates each in primary samples and in 4 technical replicates of the the DBTRGFL patient derived xenograft line. b) Invasion assays of patient derived xenograft (PDX) line DBTRGFL were performed with control (scrambled shRNA), PTPRZ1 knockdown (shRNA) and Rock Inhibition. Invasions were imaged every 24 hours, and Day 0 and Day 3 are shown. Quantification was performed by calculating how much of the gap was filled. Statistics were performed for both PTPRZ1 knockdown and Rock inhibition, and statistics are showing for Rock inhibition on top and PTPRZ1 knockdown below (* = p <0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001, Student’s two-sided t-test). c) Schematic of the mouse experiments performed in this study. PDX line DBTRGFL was historically generated by sampling primary tumor and propagating as a xenograft in the flank of a mouse. This tumor was then sorted for PTPRZ1 positive cells, and positive and unsorted cells of equal numbers were injected into the mouse. The cells were profiled using single-cell sequencing prior to injection, and resultant tumors were profiled after first emergence of tumor (F1) and after serial transplant (F2). d) Single-cell sequencing was performed on samples prior to and after tumor formation. Each cluster was correlated to the closest broad cell type, and is shown as a proportion of the whole. PTPRZ1+ cells give rise to cell types not present in the initial sort, including astrocytes and upper layer neurons. e) DBTRGFL is labeled with luciferase, and staining of surrounding brain tissue after serial transplantation identifies luciferase positive cells. A subset of these cells are also PTPRZ1 positive. Scale bar = 100 μM.