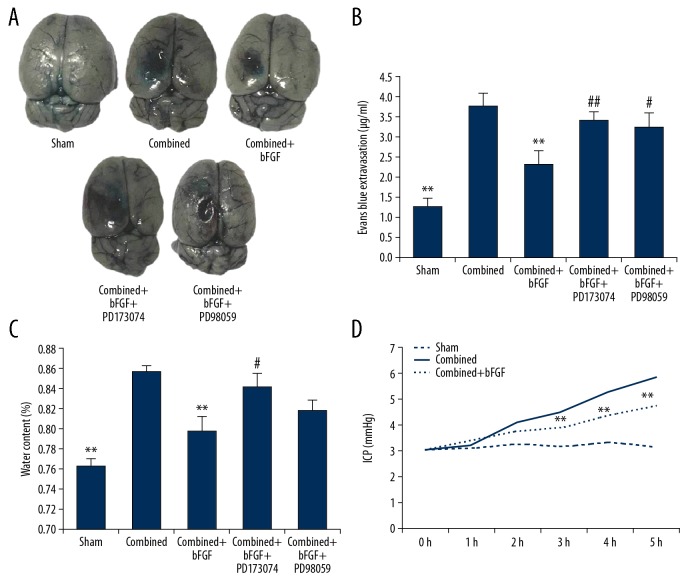
Figure 3.
bFGF reduces blood–brain barrier permeability, brain edema, and intracranial pressure. (A) Exogenous bFGF administration significantly decreased the permeability of Evans Blue dye (EB) 4 h after combined injury, which was reversed by treatment with PD173074 or PD95098. (B) Summary data showing EB extravasation. (C) Treatment with bFGF decreased the brain water content in the combined injury group samples. The protective effect of bFGF was prevented by pretreatment with PD173074 and PD95098, consistent with the EB extravasation results. (D) Treatment with bFGF decreased the intracranial pressure in combined+bFGF group rats. ** P<0.01 Sham or combined+bFGF group vs. Combined group. ## P<0.01, # P<0.05 Combined+bFGF+PD173074 or Combined+bFGF+PD98059 group vs. Combined+bFGF group. Data are presented as the mean±SD.