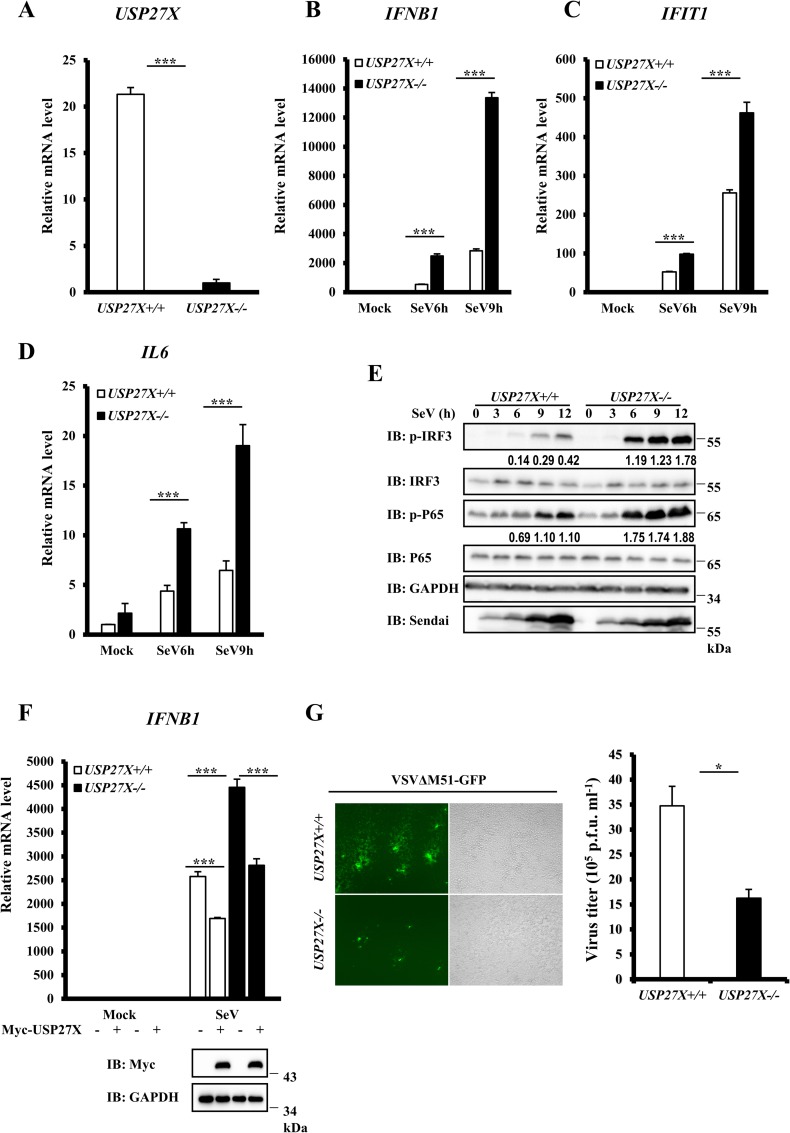
Fig 3. Knockout of USP27X increases type I IFN signaling.
(A–D) HEK293T USP27X+/+ and USP27X-/- cells were infected with SeV for the indicated times, then lysed for measurement of USP27X (A), IFNB1 (B), IFIT1 (C) and IL6 (D) mRNA levels by qRT-PCR. (E) HEK293T USP27X+/+ and USP27X-/- cells were infected with SeV for the indicated times, then lysed for immunoblotting with the indicated antibodies. (F) HEK293T USP27X+/+ and USP27X-/- cells were transfected with USP27X expression plasmid or empty vector. Twenty-four hours after transfection, the cells were infected with SeV for 9 h, followed by measurement of IFNB1 mRNA levels by qRT-PCR. (G) HEK293T USP27X +/+ and USP27X-/- cells were infected with VSVΔM51-GFP at an MOI of 0.01 for 9 h. Culture supernatants were collected to measure viral titers by plaque assay. The data shown in (A–D) and (F–G) are from one representative experiment of at least three independent experiments [mean ± SD of triplicate experiments in (A–D, F) or duplicate experiments in (G)]. The two-tailed Student’s t-test was used to analyze statistical significance. * P < 0.05; *** P < 0.001 versus control groups.