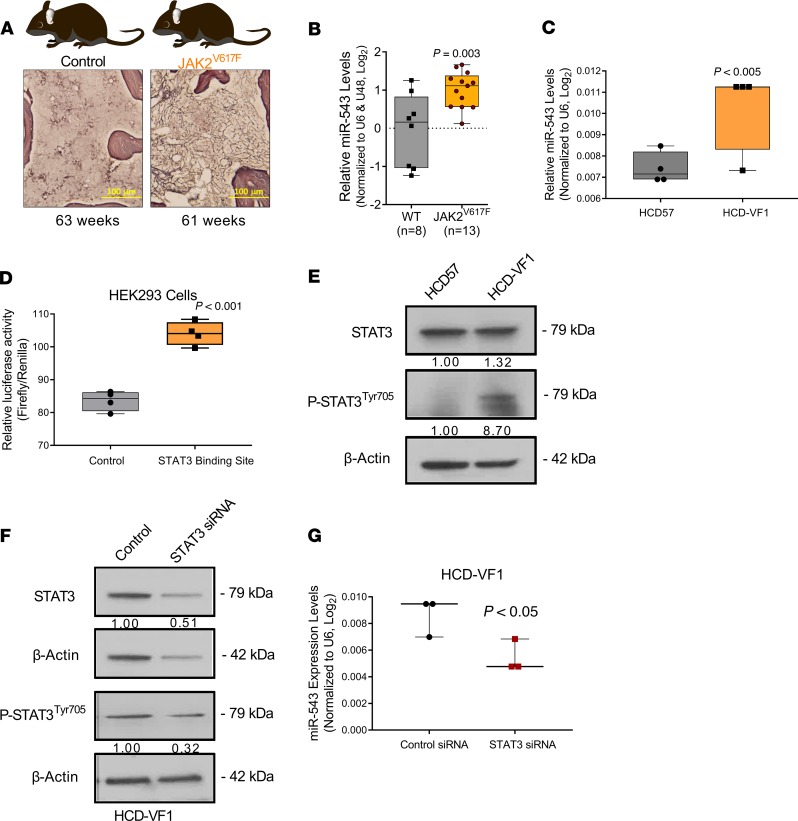
Figure 4. JAK2V617F mutation promotes increase in miR-543 levels.
(A) Representative diagram of the JAK2V617F-transgenic mouse model of MF and the representative histology slides of the BM tissue. Scale bars: 100 μm. (B) Differential expression of miR-543 measured by RT-qPCR in wild-type control mice and in JAK2V617F-transgenic mice. (C) Differential expression of miR-543 measured by RT-qPCR in the HCD57 parental control cells and HCD57 erythroleukemia cells containing the JAK2V617F mutation (HCD-VF1). U6 levels were used as normalizer. (D) Relative luciferase activity in HEK293 cells transiently cotransfected with the control vector and miR-543 promoter sequence with putative STAT3 binding site. (E) Expression levels of STAT3 and p-STAT3 Tyr705 were determined by Western blot analysis in HCD57 and HCD-VF1 cells. β-Actin was used as a loading control. (F) Expression levels of STAT3 and p-STAT3 Tyr705 were determined by Western blot analysis in HCD-VF1 cells in which STAT3 was silenced by siRNA. β-Actin was used as a loading control. (G) Silencing of STAT3 in HCD-VF1 erythroleukemia cells led to decreased miR-543 expression levels as assessed by RT-qPCR. Two-tailed t test was used to determine statistical significance for B and D. Mann-Whitney-Wilcoxon nonparametric test was used for C and E. Each dot represents 1 animal. All experiments were performed independently 3 times, and representative blots are shown.