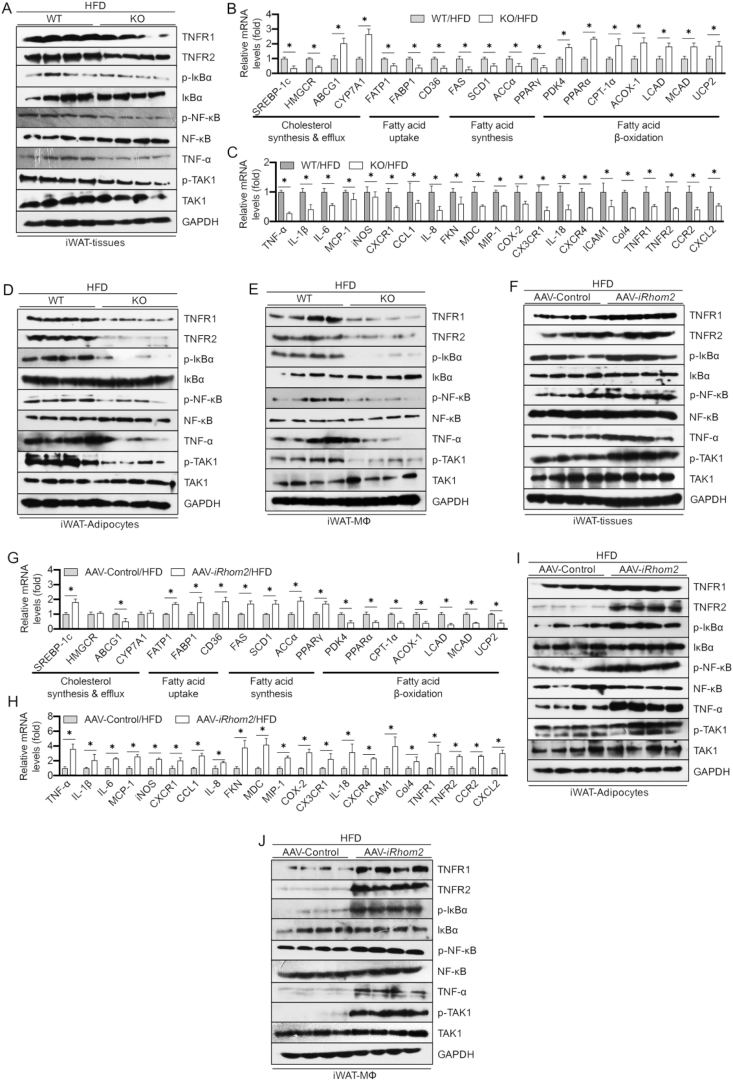
Figure 3.
iRhom2 contributes to adipose inflammatory responses in obese mice. (A) Representative immunoblot bands of the expression of inflammation-related signaling including TNFR1/2, phosphorylated IκBα, NF-κB, TAK1, and TNF-α. qPCR analysis detection of the mRNA expression of the genes responsible for (B) lipid metabolism and (C) inflammatory cytokines and chemokines in HFD-fed WT and iRhom2 mice, n = 6. Representative western blotting bands of the expression of inflammatory signaling in (D) adipocytes and (E) F4/80 ± macrophages isolated from iWAT of HFD-fed WT and iRhom2 mice. (F) Western blotting analysis of inflammatory signaling in iWAT of HFD-fed AAV-iRhom2 overactivated and corresponding mice. mRNA expression of the genes responsible for (G) lipid metabolism and (H) inflammatory cytokines and chemokines in HFD-fed AAV control and AAV-iRhom2 overactivated mice, n = 6. Western blotting of the expression of inflammation indicators in (I) adipocytes and (J) F4/80 ± macrophages from iWAT of AAV control and AAV-iRhom2 overactivated mice. The data are expressed as mean ± SEM, *p < 0.05.