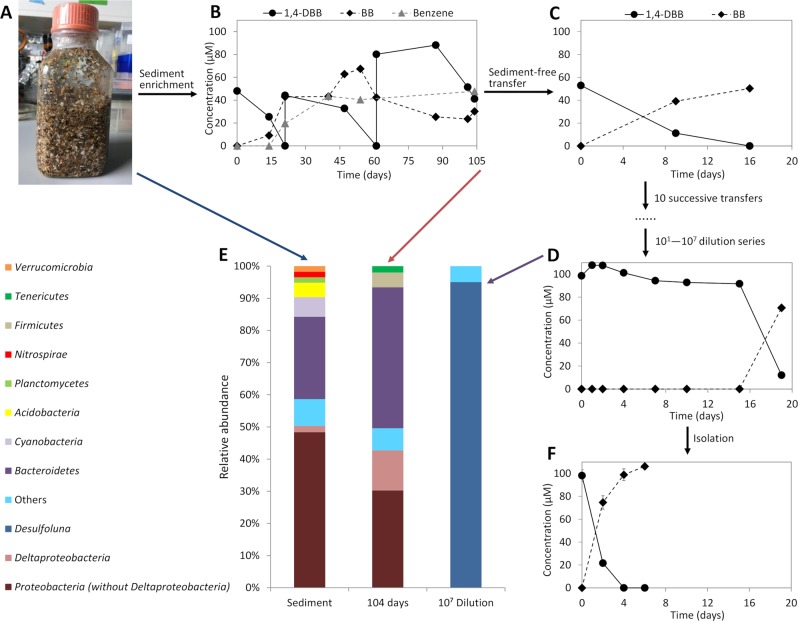
Fig. 1. Enrichment and isolation of D. spongiiphila DBB.
Intertidal sediment mainly composed of shore sediment used for isolation (a). Reductive debromination of 1,4-dibromobenzene (1,4-DBB) by: the original microcosms containing intertidal sediment (b), the sediment-free enrichment cultures (c), the most diluted culture (107) in the dilution series (d). Phylogenetic analysis of bacterial communities in the microcosms from the shore sediment at time zero (left), the original 1,4-DBB debrominating enrichment culture after 104 days incubation (middle) and the 107 dilution series culture (right) (e). Reductive debromination of 1,4-DBB to bromobenzene (BB) by the isolated pure culture (f). Sediment enrichment culture and sediment-free transfer cultures (b–d) were prepared in single bottles. Pure cultures (f) were prepared in duplicate bottles. Points and error bars represent the average and standard deviation of samples taken from the duplicate cultures. Phylogenetic data are shown at phylum level, except Deltaproteobacteria shown at class level and Desulfoluna at genus level. Taxa comprising less than 1% of the total bacterial community are categorized as ‘Others’.