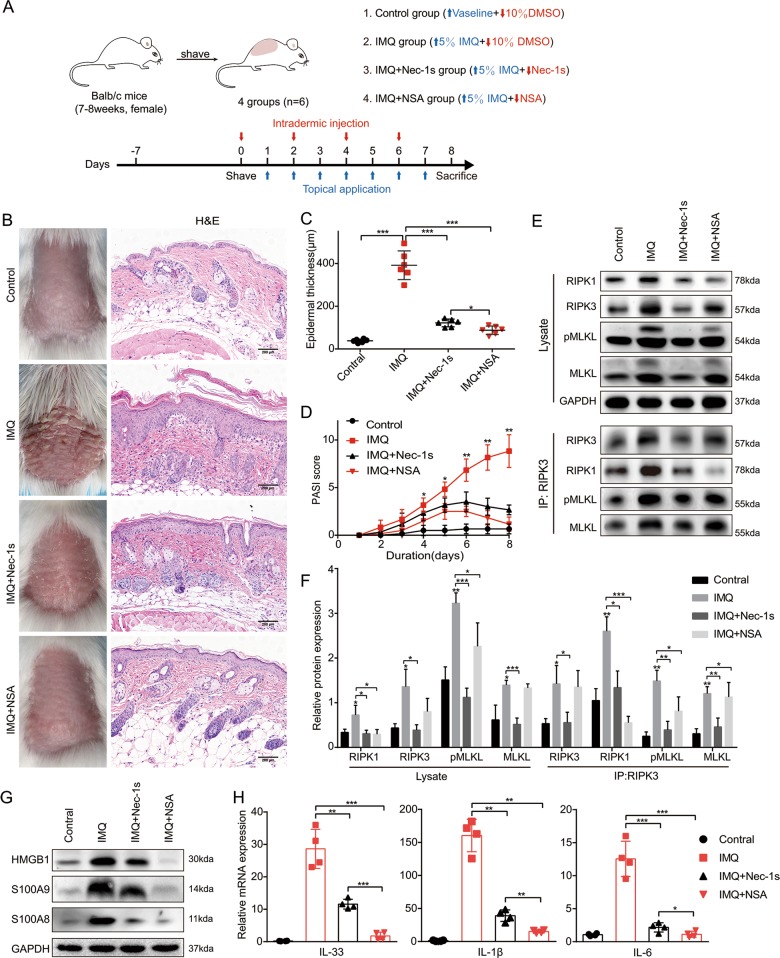
Fig. 7. NSA achieved more benefits than Nec-1s on reducing inflammation in mice with IMQ-induced psoriasiform dermatitis.
a Schematic representation of the animal experiment protocol for the Control, IMQ, IMQ + Nec-1s and IMQ + NSA groups (n = 6). b Representative macroscopic images taken on the 8th day and H&E staining of cross-sectional slices of the dorsal skin of BALB/c mice following continuous treatment for 8 days. c Epidermal thickness of the dorsal skin on the 8th day was calculated on four randomly selected optical fields per section of each mouse. d Daily assessment of epidermal erythema, scaling and thickening of the dorsal skin. PASI score was calculated by adding the scores of the three separate criteria (range from 0 to 12). e, f Protein levels of RIPK1, RIPK3, MLKL and pMLKL (S345) were analyzed by western blotting. GAPDH was used as a loading control. The whole lysates in the four groups was immunoprecipitated with anti-RIPK3 antibody, followed by immunoblotting of RIPK1, RIPK3, MLKL, and pMLKL (S345). g Protein levels of HMGB1, S100A8 and S100A9 were analyzed by western blotting. h Real-time quantitative PCR analysis was performed to determine the mRNA expression levels of IL-33, IL-1β, and IL-6 in skin biopsies from mice. Results shown are representative data of three independent experiments. Error bars represent mean ± standard deviation (SD). *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, and ***p < 0.001 when compared.