Fig. 2. Relative abundance of ZOTUs, collapsed at the genus level (delimited by black lines), and classified as core, pepper field specific, watermelon field specific, starting population specific (Watermelon_0), and genera shared between pairwise combinations according to their presence among B. tabaci gut-enriched samples.
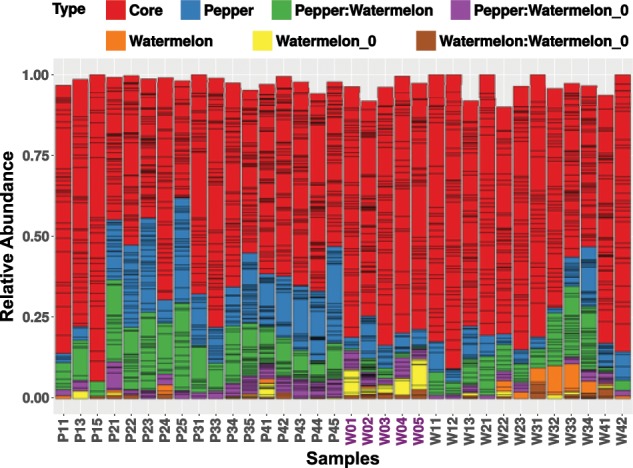
ZOTUs were classified as core, shared, or specific and were considered part of a certain group only if they were present in at least two samples of each of the subgroups of the main presented biological group. For example, the pepper field-specific main group included four subgroups (generations 1–4). Note that ZOTUs associated with the same group (e.g., pepper field-specific) are coded by the same color (e.g., blue), and may also appear, in a nonconsistent matter, in samples associated with a different biological group. Therefore, although the “blue” labeling appears in all samples, it stands, in each of the non-pepper samples, for different ZOTUs. Summed relative abundance does not reach 1 in some samples as sample-specific ZOTUs were excluded.
