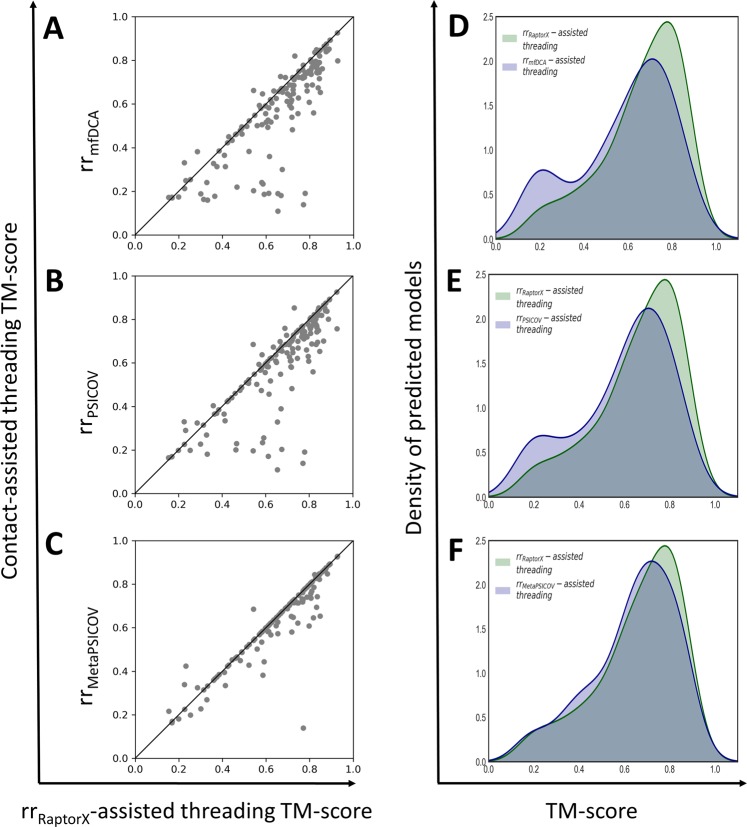
Figure 3.
A head-to-head comparison of different contact-assisted threading methods and baseline RaptorX-assisted threading method on PSICOV150 dataset. (A) mfDCA-assisted threading method (referred to as rrmfDCA) versus baseline RaptorX-assisted threading method (referred to as rrRAPTORX-assisted threading), (B) PSICOV-assisted threading method (referred to as rrPSICOV) versus baseline RaptorX-assisted threading method, (C) MetaPSICOV-assisted threading method (referred to as rrMetaPSICOV) versus baseline RaptorX-assisted threading method. Each point in each scatter plot represents joint TM-score of top ranked model predicted by baseline RaptorX-assisted threading and one of the other three contact-assisted threading methods respectively. (D) TM-score distribution of top ranked models predicted by RaptorX-assisted threading method versus mfDCA-assisted threading method (referred to as rrmfDCA-assisted threading), (F) TM-score distribution of top ranked models predicted by RaptorX-assisted threading method versus PSICOV-assisted threading method (referred to as rrPSICOV-assisted threading), (G) TM-score distribution of top ranked models predicted by RaptorX-assisted threading method versus MetaPSICOV-assisted threading method (referred to as rrMetaPSICOV-assisted threading). Templates with sequence similarity >30% to the query sequence are excluded.