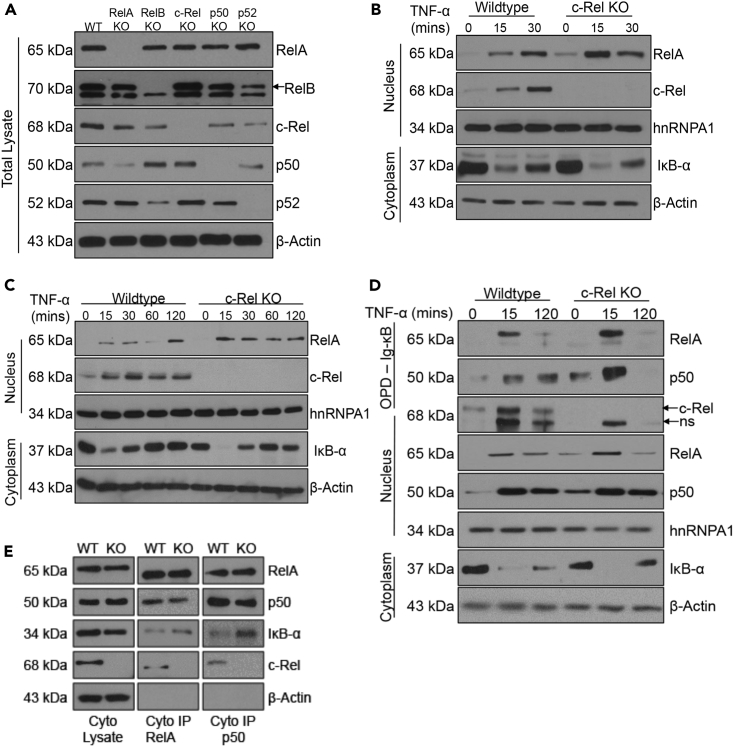
Figure 4.
c-Rel Knockout Enhances TNF-α-Induced Nuclear Translocation and DNA Binding of RelA
(A) Total cell lysates of wild-type and the knockouts of RelA, RelB, c-Rel, p50, and p52 MEFs were analyzed with antibodies to each of the indicated NF-κB proteins. Actin was used as the loading control.
(B) Wild-type or c-Rel knockout MEFs were left untreated or treated with 100 ng/mL TNF-α for 15 or 30 min. Nuclear and cytoplasmic extracts were analyzed with antibodies against the indicated proteins. hnRNPA1 was used as the loading control for nuclear fraction, and actin was used as the loading control for cytoplasmic fraction.
(C). Primary bone marrow-derived macrophages generated from wild-type or c-Rel knockout mice were left untreated or stimulated with 100 ng/mL TNF-α for the indicated time points. Nuclear and cytoplasmic extracts were analyzed with antibodies against the indicated proteins.
(D) Wild-type or c-Rel knockout MEFs (3 × 106 at time of harvest) were left untreated or treated with 100 ng/mL TNF-α for 15 or 120 min. Nuclear and cytoplasmic extracts were prepared, and 100 μg of nuclear proteins per sample was utilized in an in vitro pull-down assay using biotinylated Ig-κB oligonucleotide. The precipitated proteins were separated in SDS/PAGE gel and probed for RelA, p50, and c-Rel. ns indicates non-specific band. Nuclear and cytoplasmic extracts were also probed using the indicated antibodies to examine the extent of their nuclear translocation as well as the degradation of IκB in the cytoplasm.
(E) Cytoplasmic extracts were prepared from wild-type or c-Rel knockout MEFs. Cytoplasmic lysates and immunoprecipitates of RelA and p50 antibodies were analyzed with the antibodies against indicated proteins.
Data for (A), (B), (D), and (E) are representative of four independent experiments, and C is representative of three independent experiments. See also Figure S4.