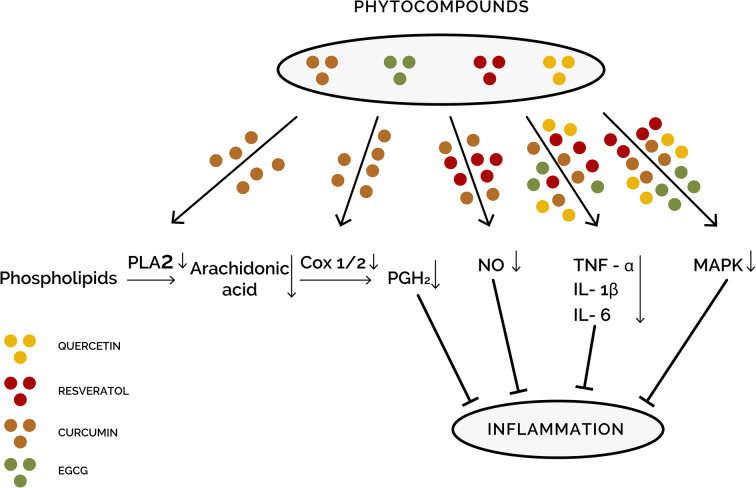
Fig. 2.
Schematic representation of inflammation-related molecular pathways potentially affected by PBC-loaded NPs. The anti-inflammatory effects of such NPs might be mediated through inhibiting the production of nitric oxide (NO) by nitric oxide synthase (iNOS), lowering the levels of prostaglandins and arachidonic acid metabolites through inhibiting phospholipase A2 (PLA2) and cyclooxygenase (COX) pathways, or down-regulating the mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) and nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB) pathways