Figure 1.
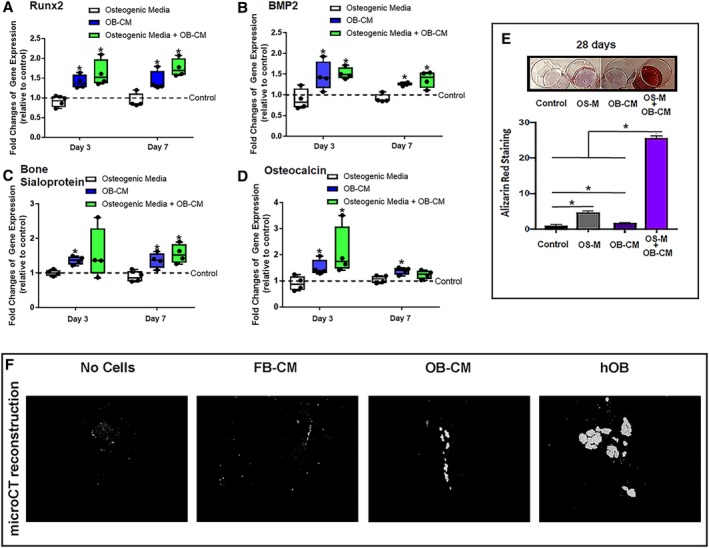
Human OB‐conditioned media converts human fibroblasts into osteoblasts. Fibroblasts were treated with OB‐CM, OS‐M, or in combination (OB‐CM+OS‐M). The expression level of osteogenic markers, Runx2, BMP2, bone sialoprotein, and osteocalcin, was measured by qPCR after 3 and 7 days of culture. OB‐CM or OB‐CM+OS‐M significantly increased expression of osteogenic genes in fibroblasts (A‐D). Matrix mineralization in cells was detected by Alizarin Red S staining after 28 days of treatment. Fibroblast treated with OB‐CM+OS‐M exhibited greatest mineralization with an over 20‐fold increase compared to control treatment (FB‐CM) (E). OS‐M, osteogenic components; OB‐CM, osteoblast‐derived conditioned media. F, Fibroblasts treated with OB‐CM or FB‐CM were implanted into nude mice using a carrier of Matrigel and ceramic microparticles. Mineralized tissue was analyzed by MicroCT for the total volume of mineralized bone tissue (BV). MicroCT analysis of mineralized bone (0.2 g/cm3 threshold) showed abundant bone formation with implanted human osteoblasts, and some mineralization was observed in the mice implanted with OB‐CM treated fibroblasts, but no mineralization was observed in no cell and FB‐CM treated fibroblasts implantation controls. Dashed line: control (fibroblast‐derived conditioned media, FB‐CM). *P ≤ .05 using ANOVA. Data were replicated in four independent experiments
