Fig. 1.
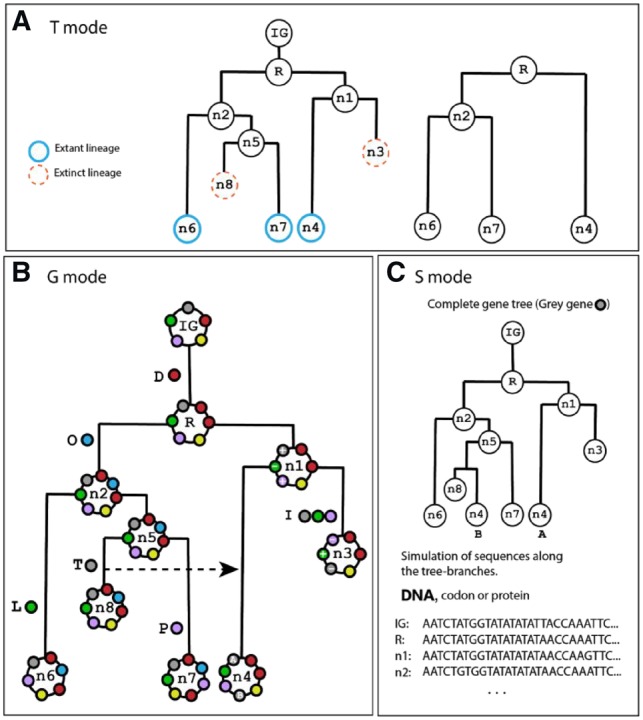
Overview of the three steps of the Zombi simulator. (A) In T mode, Zombi simulates a species tree using a birth-death process and outputs the pruned version of it by removing extinct lineages. In this example, lineages n3 and n8 go extinct before the simulation ends. (B) in G mode, a circular genome evolves within the branches of the complete species tree obtained with the T mode by Duplications (D), Originations (O), Inversions (I), Transpositions (P), Losses (L) and Transfers (T) of genes. The simulation starts with the initial genome (IG) containing a number of genes determined by the user (5 in this example, represented by the coloured circles). Each gene has an orientation (+ or -) that is determined randomly and represents the direction of the gene in the coding strand. Several events affecting different genes and their impact on the genome structure are indicated next to the branches where they occur. The inversion events not only modify the positions of the genes but also change their orientation. (C) In S mode, Zombi can be used to simulate codon, nucleotides and amino acids along the branches of the gene family trees. Here, the gene tree of the grey coloured gene family from B has been depicted
