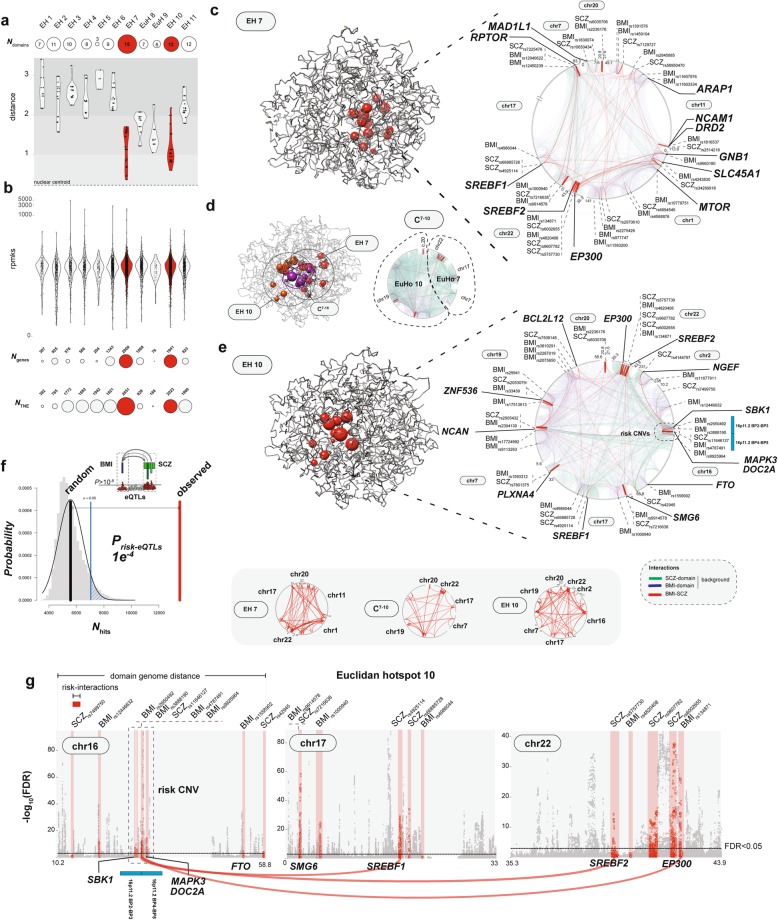
Fig. 3.
Euclidean hot spot analysis. a Violin plot representing each of the 11 EH, showing distance of domain-to-nuclear centroid. Scaled circles represent the number of domains found in each EH. Red color represents EHs no.7 and no.10 harboring the largest number of domains, as indicated. b Violin plot representing rpmks gene expression levels per EH, circle plots showing number of genes (Ngenes) and number of transcribed non-coding elements (NTNE) per EH, as indicated. Note that EH no. 7 and no. 10 (red) represent transcriptionally active domain clusters. c–e In silico chrom3D models of MDN spatial genome, red beads = EH-specific domains, c EH no. 7, d pink beads = cluster C (from Fig. 2e) domains shared among EH no. 7 and no. 10, and e EH no. 10. Circos plot interactomes for (c, right panel) EH no.7 and (d, right panel) cluster C(7,10) and (e, right panel) EH no. 10, showing for each participating chromosome the location of (red tick marks) risk SNPs and (red lines) Hi-C Pro called chromosomal contacts reciprocally interconnecting BMI-to-SCZ risk variants at 40 kb resolution, including position of selected target genes. “Background chromosomal contacts” (blue) mark “BMI risk variant-to-rest of EH” contacts and (green) “SCZ risk variant-to-rest of EH” contacts, using BMI and SCZ index SNPs (Additional file 2: Table S4). f Permutation analysis probability density plot. The likelihood of cross disorder BMI-to-SCZ reciprocal interactions associated to significant brain cis-eQTLs (called at FDR < 10−8) was performed by comparing the association of randomized cross-disorder interactions (10,000 permutations) over the observed overlap. g Representative brain cis-eQTLs Manhattan plots shown for three domains from EH no. 10. Red shaded fields mark sequences fulfilling each of the following three conditions: (i) harboring both SCZ and BMI risk polymorphisms, (ii) anchored in cross-disorder chromosomal contact within the EH, and (iii) harboring significant brain cis-eQTLs. As an example, highlighted by red connector lines scaled to the ICED interaction frequency, interactions anchored in chr1611p2B2-B3/B4-B5 locus implicated in weight regulation and neurodevelopment [87] to disease-relevant associated genes SREBF1, SREBF2, and EP300