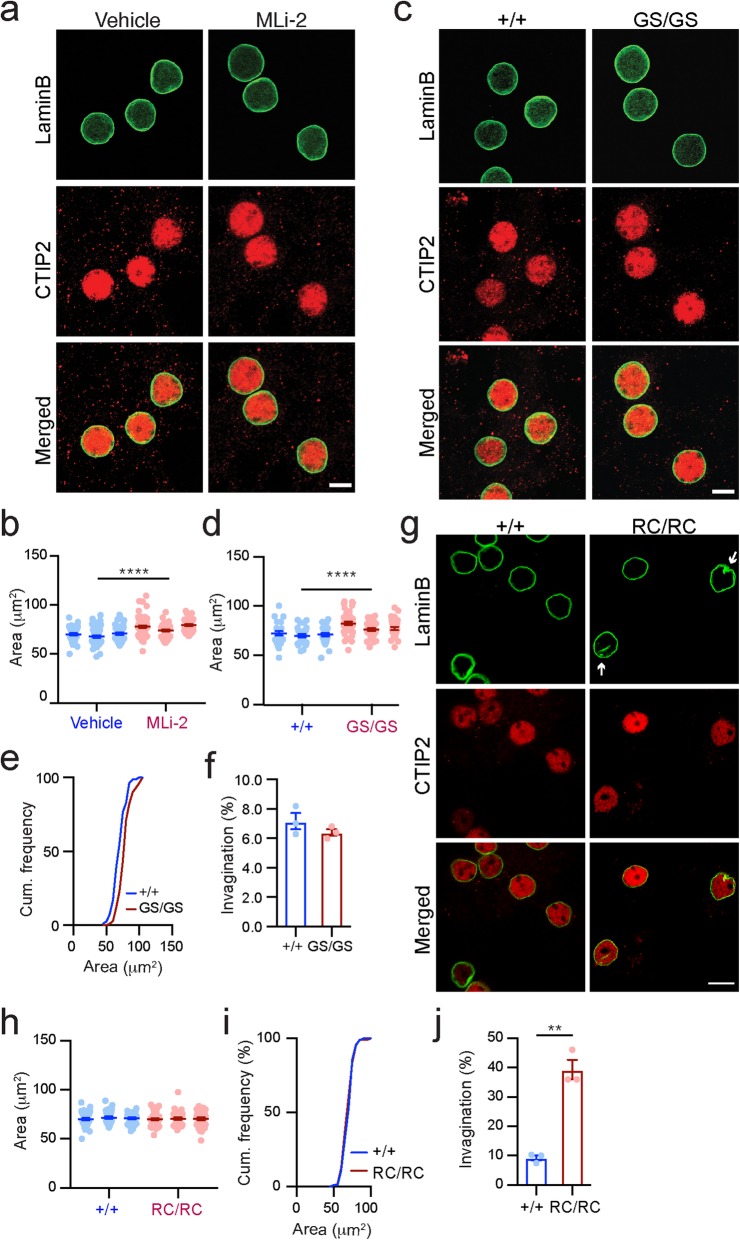
Fig. 8.
The malfunction of LRRK2 kinase and GTPase domains induces differential nuclear morphological alterations. a, b Co-staining of Lamin B and CTIP2 in 3-week Lrrk2+/+ SPN cultures treated with vehicle or MLi-2 (a). Scale bar, 5 μm. The area of SPN nuclei was measured from three independent Lrrk2+/+ cultures (b). N = 150 neurons per treatment. Conditional logistic regression test, ****p < 0.0001. c Co-staining of Lamin B and CTIP2 in the Lrrk2+/+ and Lrrk2 G2019S SPNs after 3 weeks in culture. Scale bar, 5 μm. d-f The area of SPN nuclei was measured from three independent Lrrk2+/+ and Lrrk2 G2019S cultures (d). N = 100 neurons per genotype. Conditional logistic regression test, ****p < 0.0001. Cumulative (Cum.) frequency was calculated to show the nuclear size distribution in each genotype (e). Ratio of SPN nuclei containing ≥1 invagination was calculated from three independent Lrrk2+/+ and Lrrk2 G2019S cultures (f). N = 100 neurons per genotype. Paired t-test, no statistically significant difference was identified. g Co-staining of Lamin B and CTIP2 in Lrrk2+/+ and Lrrk2 R1441C SPNs after 3 weeks in culture. Scale bar, 5 μm. h-j The area of SPN nuclei was measured from three independent Lrrk2+/+ and Lrrk2 R1441C cultures (h). N = 100 neurons per genotype. Conditional logistic regression test, no statistically significant difference was identified. Cumulative (Cum.) frequency was calculated to show the nuclear size distribution in each genotype (i). Ratio of SPN nuclei containing ≥1 invagination was calculated from three independent Lrrk2+/+ and Lrrk2 R1441C cultures (j). N = 100 neurons per genotype. Paired t-test, **p = 0.0092