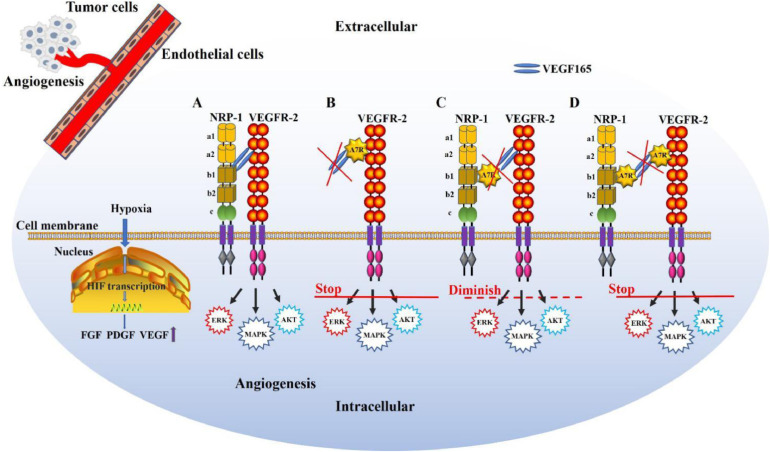
Fig. 3.
Roles of VEGFR-2 and NRP-1 in angiogenesis and the antiangiogenic mechanism of action of A7R. Hypoxia increases cellular hypoxia inducible factor (HIF) transcription, leading to the upregulation of FGF, PDGF, and VEGF expression in endothelial cells. (A) NRP-1 functioning as a coreceptor binds to VEGF165 and enhances VEGF165-VEGFR-2 intracellular trafficking, facilitating angiogenesis. (B) A7R can target and compete with VEGF165 to bind VEGFR-2 and suppress the downstream signal transduction of VEGFR-2. (C) A7R can bind to the b1 domain of NRP-1, inhibit VEGF165 binding to NRP-1 and diminish VEGF165-VEGFR-2 intracellular trafficking. (D) A7R can bind preferentially to both VEGFR-2 and NRP-1 simultaneously and suppress the signal transduction downstream of VEGFR-2, displaying the strongest antiangiogenic activity.