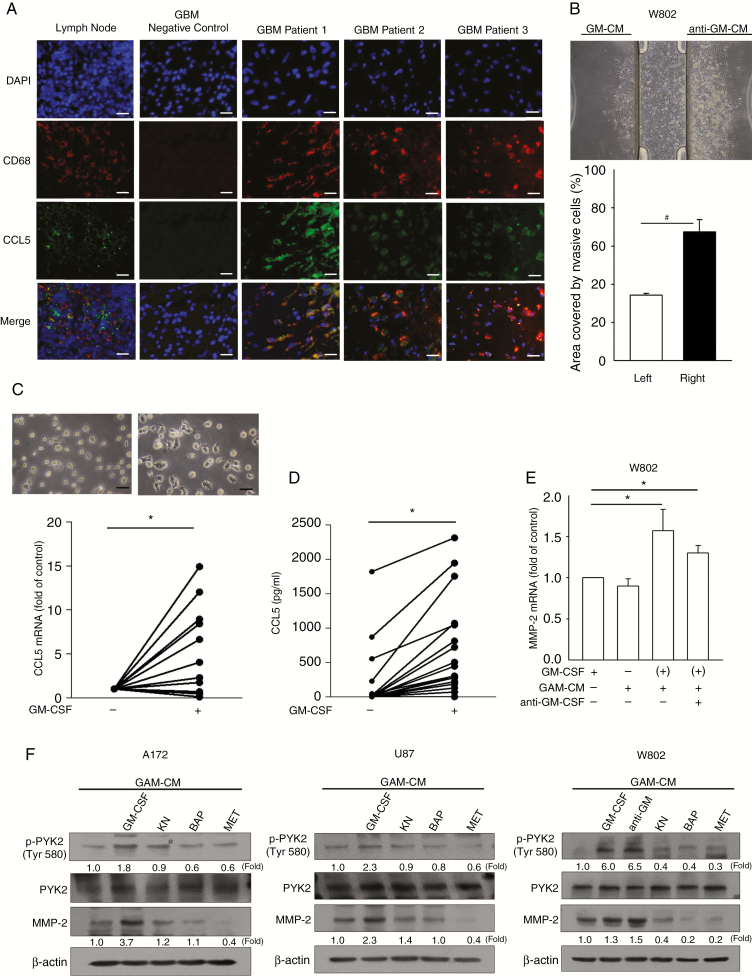
Fig. 6.
The increased MMP2 expression by GM-CM is suppressed by inhibition of calcium-related signaling pathways. (A) IHC staining of CD68 (red), CCL5 (green), and DAPI (blue) in newly diagnosed GBM tumor sections (n = 3). (B) W802 cells invaded toward the reservoir containing anti–GM-CM. Percentages of areas covered by invading W802 cells are shown. (C) Representative images of GAMs stimulated with or without GM-CSF, which showed that the CCL5 mRNA level was increased in GM-CSF–stimulated GAMs (n = 21). (D) The amounts of CCL5 in CM and GM-CM were Figure 6 Continued.determined (n = 21). (E) MMP2 mRNA expression in glioma cells was determined after 24 h of treatment with CM or GM-CM. (F) Glioma cells pretreated with KN, BAP, or MET prior to GM-CM or CM treatment showed downregulation of PYK2 phosphorylation and cleaved MMP2 protein expression. “(+)” represents CM collected from GM-CSF–activated GAMs. Bar: 100 µm. All data are presented as means ± SE. *P < 0.05, #P < 0.01. Blots are quantified as fold of control.