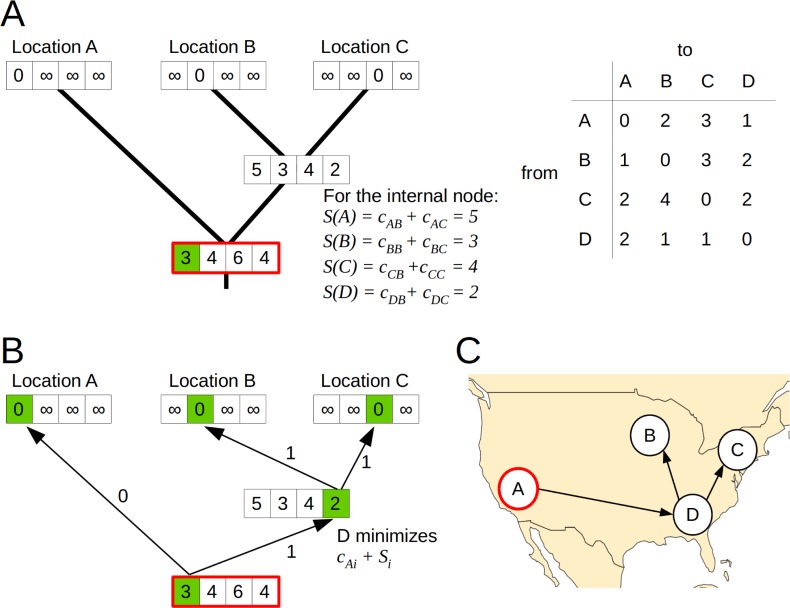
Fig 2. Phylogeographic reconstruction with the Sankoff algorithm using asymmetric, effective distances.
Exemplary phylogeographic reconstruction using the Sankoff algorithm on the tree and the cost matrix shown in panel A. The cost matrix c is asymmetric and represents effective distances. For each internal node, the Sankoff algorithm calculates the minimal cost S(i) in the subtree, given the node is assigned location i (shown as the arrays in A, calculated via S(i) = minj[cij+Sl(j)]+mink[cik+Sr(k)], where l and r denote the two descendant subtrees, and their costs, Sl(j) and Sr(k), respectively. For the root (shown in red), location A results in the minimal cost and is assigned to that node (marked in green). Backtracking from the root to assign all other locations is shown in panel B. Given that a parent node has been assigned state j, the child node will be assigned the state i that minimizes cji+S(i). The result of the backtracking is indicated by arrows labeled with the costs and the states marked in green. The reconstructed spread along the tree is shown on a map in panel C.