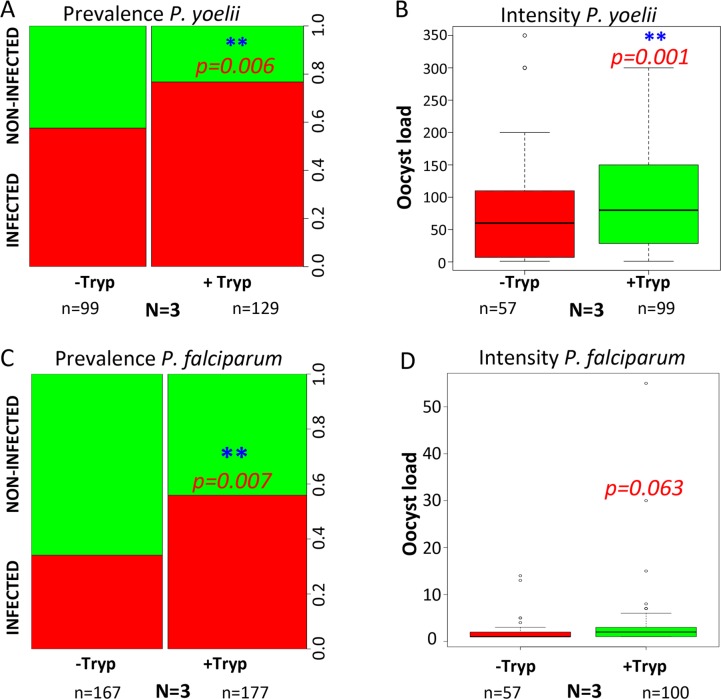
Fig 4. A first infectious blood meal with T. b. brucei increases mosquito susceptibility to rodent and human malaria parasites.
Panels (A) & (B) show results of infection prevalence and infection intensity for P. yoelii, respectively. Panels (C) & (D) show results of infection prevalence and infection intensity for P. falciparum, respectively. -Tryp = group of mosquitoes previously fed on a naive mouse (without Trypanosoma parasites); +Tryp = group of mosquitoes previously fed on a Trypanosoma-infected mouse. **: Combined p-value <0.01 (Fisher method) from the 3 independent biological replicates obtained for the infection prevalence (p = 0.006 for P. yoelii; p = 0.007 for P. falciparum) and for infection intensity (p = 0.001 for P. yoelii only). n = Total number of dissected mosquitoes. N = number of biological replicates.