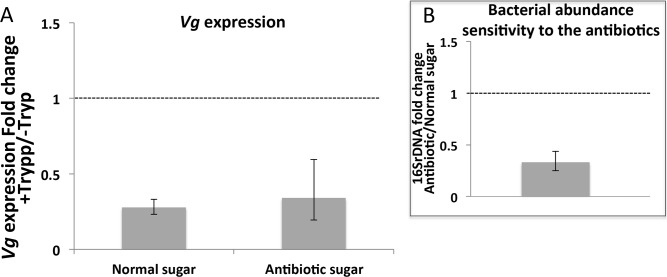
Fig 7. Decreased expression of vitellogenin in T. b. brucei infected background is not dependent on the bacterial abundance increase.
(A) Vitellogenin (Vg) expression level was quantified by qPCR in “Normal sugar” and “Antibiotic sugar” backgrounds from mosquito samples fed on a naive mouse (-Tryp) or on a Trypanosoma-infected mouse (+Tryp). Each bar of the graph shows median fold change of vitellogenin expression in mosquitoes fed on mice infected by Trypanosoma (+Tryp) as compared to those fed on naive mice (doted line). The ribosomal protein rps7 gene was used as an internal calibrator. The ratio of the normalized Vg expression in “+Tryp” versus “-Tryp” was calculated using triplicates from the same cDNA dilution. *: Statistically significant p-value (p<0.05) related to the deltaCt distribution between “+Tryp” and “-Tryp”. (B) Antibiotic efficiency on the bacterial abundance was verified by measuring the abundance of the bacteria (by qPCR detection of 16S rDNA) between “Antibiotic sugar” and “Normal sugar” (doted line) backgrounds 24h post-blood meal. The ratio of the normalized 16S rDNA detection in “Normal sugar” versus “Antibiotic sugar” backgrounds was computed using triplicates from the same cDNA dilution. In A & B, error bars show median absolute deviation computed by permutation from 3 independent biological experiments.