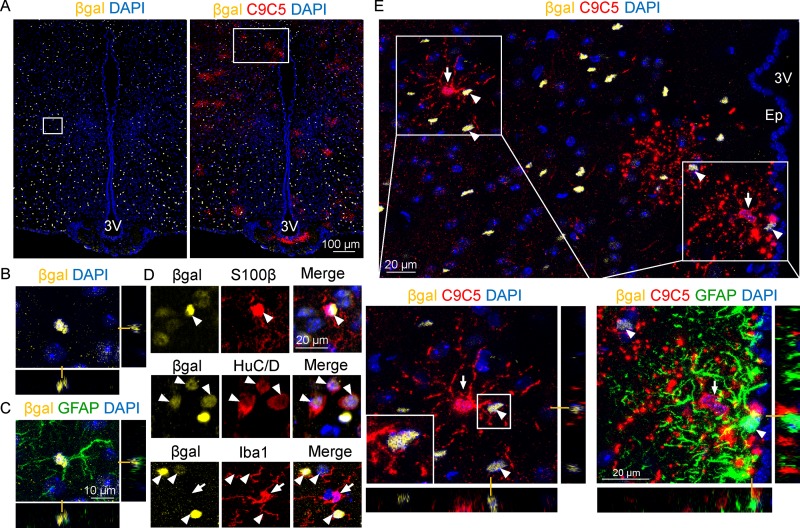
Fig 5. C9C5+ cells delineate Shh expression domains containing Ptc-expressing cells.
(A-E) Fluorescence confocal (A-C, E) imaging of βgalactosidase (βgal), C9C5, GFAP, S100β, HuC/D, and Iba1 immunostaining on coronal brain sections of adult PtcLacZ/+ mouse hypothalamus at the level of the median eminence. (A, E) Detection of βgal signal (yellow) alone and together with C9C5 signal (red) indicated wide distribution of Ptc-expressing cells in hypothalamic nuclei. (B-C) Orthogonal views of the magnified white square (A, left) showing co-localization of βgal and the astroglial marker GFAP. (D) High magnifications of the hypothalamic parenchyma from independent experiments showing colocalization of βgal (white arrowheads) with the astroglial marker S100β or with the neuronal marker HuC/D, but not with the microglial marker Iba1 (white arrow). (E) White square magnification (from A, right) showing C9C5+ cell bodies (white arrows) delineating Shh expression domains in the parenchyma and next to the ependymal layer (Ep) of the third ventricle (3V). White boxes highlight magnifications with orthogonal views of C9C5+ processes contacting βgal+ Ptc-expressing cells (white arrowheads). Staining was replicated on four mice. Nuclei stained with DAPI.