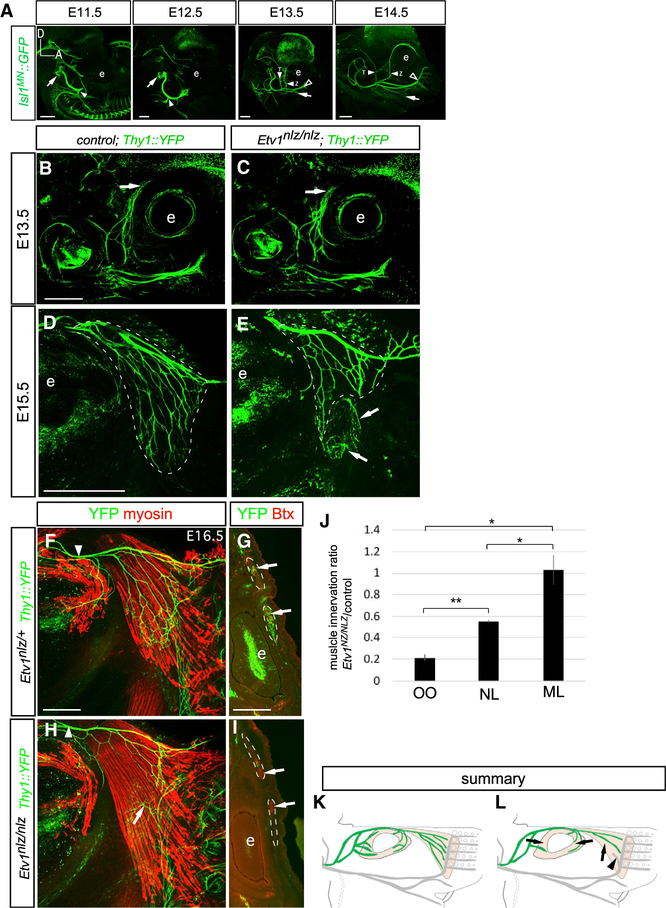
Figure 6. Attenuation of DL Facial Motor Subnucleus Target Muscle Innervation in Etv1-Mutant Mice.
(A) Time course of embryonic facial nerve development from E11.5 to E15.5. GFP immunostaining in embryonic Isl1MN::GFP mice. Arrows at E11.5 and E12.5 indicate the exit of the facial nerve from the pons. The ramification of the auricular (filled arrowheads at E11.5 and E12.5), zygomatic/temporal (filled arrowheads at E13.5 and E14.5), buccolabial (open arrowheads at E13.5 and E14.5), and marginal mandibular branches (arrows at E13.5 and E14.5) are indicated. Eye is marked with “e”; dorsal (D) and anterior (A) directions are indicated.
(B–E) Z/T axon growth in wild-type (B and D) and Etv1 mutant (C and E) embryos at E13.5 (B and C) and E15.5 (D and E). Z/T branch growth is unchanged in Etv1 mutants at E13.5 (B and C), but attenuation of NL innervation is apparent by E15.5 (dotted lines in D and E). Arrows in (E) mark ectopic innervation of the NL by BL nerve-branch fibers.
(F and H) GFP (green) and myosin (red) immunostaining on whole-mount NL muscles from control (F) and Etv1−/−(H) E16.5 Thy1::YFP embryos. NL innervation remains attenuated, arrow in (H) marks the ectopic invasion of the ventral NL by the BL nerve-branch fibers. No obvious change in Z/T facial nerve-branch caliber was observed in Etv1-mutant embryos, arrows in (B) and (C) and arrowheads in (F) and (H).
(G and I) GFP immunofluorescence (green) and Alexa555 bungarotoxin (Btx, red) staining on coronal cross sections through nasal OO from control (G) and Etv1-mutant (I) Thy1::YFP mice at E16.5. OO innervation is reduced in Etv1 mutants; dotted lines denote OO muscle, arrows label regions of OO innervation in the control muscle that is absent from the Etv1 mutant.
(J) NL and OO muscle innervation is reduced in Etv1-mutant mice, represented as the means of the ratio of muscle innervation detected in Etv1nlz/nlz compared with littermate controls. Innervation of the maxillolabialis (ML) muscle supplied by the BL nerve branch is unchanged. n = 3 embryos per genotype (unpaired t test, *p < 0.05, **p < 0.005). Samples were cleared for imaging using iDISCO (A) or BABB (B–I); see Method Details.
(K and L) Summary of reduced innervation of the NL and OO muscles (shaded tan) by Z/T facial-nerve fibers (green) in Etv1 mutants. Arrowhead in (L) indicates BL fibers from the L subnucleus mistargeted to the NL.
Scale bars: 500 μm in (A)–(E), 250 μm in (F) and (H), and 500 μm in (G) and (I).
See also Figure S5.