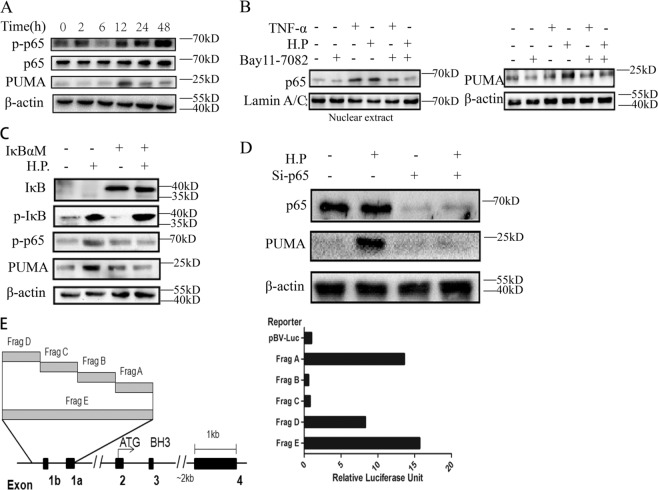
Fig. 4. P65 directly binds to the PUMA promoter to activate its transcription following H. pylori treatment.
a Expression of p-p65 (S536), p65, and PUMA on AGS cells after treatment with H. pylori at the indicated time points was analyzed by western blotting. b AGS cells were treated with 10 mmol/L BAY 11–7082 for 1 h and then with H. pylori or 10 ng/mL TNF-α for 24 h. Left, nuclear fractions were isolated from cells and analyzed for p65 expression by western blotting; right, western blot analysis of PUMA and β-actin expression in whole-cell lysates after H. pylori or TNF-α treatment. c WT AGS cells were transfected overnight with pCMV or IκBαM and then treated with H. pylori for 24 h. The expression levels of PUMA, p-IκB, IκB, and p-p65 were analyzed by western blotting. d AGS cells were transfected with either a control scrambled siRNA or a p65 siRNA for 24 h and then treated with H. pylori for 60 h. p65 and PUMA expression was probed by western blotting. e Left, schematic representation of the genomic structure of PUMA highlighting the PUMA promoter fragments (Frag) A–E of the PUMA promoter, followed by treatment with H. pylori. Reporter activities were measured 24 h later by a luciferase assay.