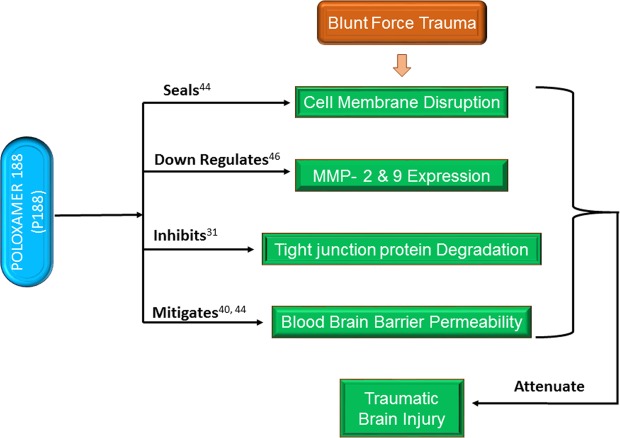
Figure 13.
Schematics showing the potential mechanisms underlying the protective effects of P188. Blunt force trauma increases ROS. The oxidative stress-sensitive signaling pathways (e.g., NF-kB) can up-regulate MMP- 2 & 9 in the brain endothelium which, in turn, degrades the tight junction structure and integrity. The brain endothelium transport properties are modulated and lead to an increased BBB permeability. The BBB protection by P188 against traumatic brain injury is proposed to be mediated by resealing the compromised cell membrane, decreasing the ROS levels, down-regulating MMPs, which inhibits the degradation of tight junction, and thereby restores the biotransport properties of the brain endothelium. Collectively, P188 attenuates the extent of injuries caused by blunt force brain traumas.