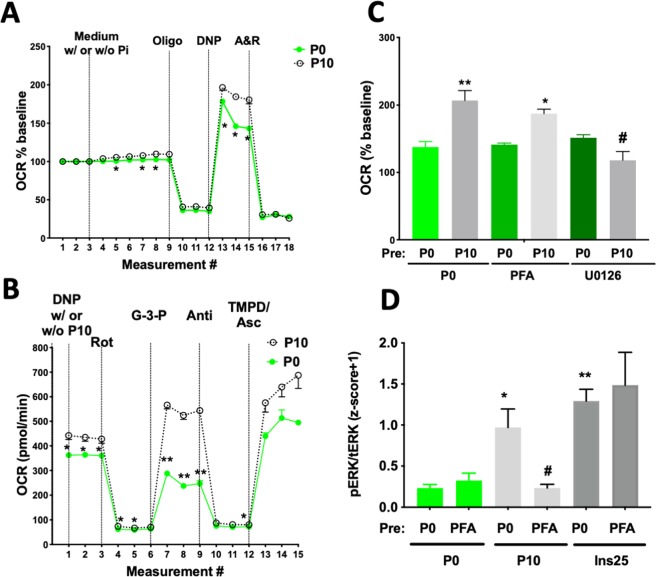
Figure 5.
Respiratory chain activity of C2C12 cells. (A) Individual tracing of a coupling assay using intact C2C12 cells and a Seahorse XFe24 analyzer showed reduced oxygen consumption rate (OCR) in cells deprived of Pi (P0) when compared to cells exposed to 10 mM Pi (P10). (B) Individual tracing of a mitochondrial electron-flow assay in permeabilized C2C12 cells in the absence (P0) and in the presence of 10 mM Pi (P10). To stimulate individual complexes, 1 nM Plasma Membrane Permeabilizer (Seahorse) and 100 nM dinitrophenol (DNP) was used along with 10 mM pyruvate/1 mM malate (complex C-I), 1 uM rotenone/10 mM glycerol-3-phosphate (complex C-III) or 10 mM ascorbate/100 nM N,N,N',N'-tetramethyl-1,4-phenylenediamine (TMPD) (complex C-IV), respectively. (C) Summary of several coupling assays as described in A. Pre-treatment with phosphonoformic acid (5 mM PFA), an inhibitor of Pit1, and U0126 (30 uM), an inhibitor of MEK1/2, the kinase upstream of ERK1/2, attenuated the Pi-dependent increase in maximal respiration (D) Summary of several immunoblots of C2C12 lysates following pre-treatment with 5 mM PFA which inhibited stimulation of pERK1/2 by 10 mM Pi (P10), but not by 25 uM human insulin (Ins25). Densitometric results were averaged following z-score transformation of the of individual blots. Shown are means ± SEM, n = 3–5, ****p < 0.00002, ***p = 0.0002, **p = 0.002, *p = 0.03 vs. pre-P0/P0. #p = 0.03 vs. pre-P0/P10 (C) and vs. pre-P0/P10 (D).