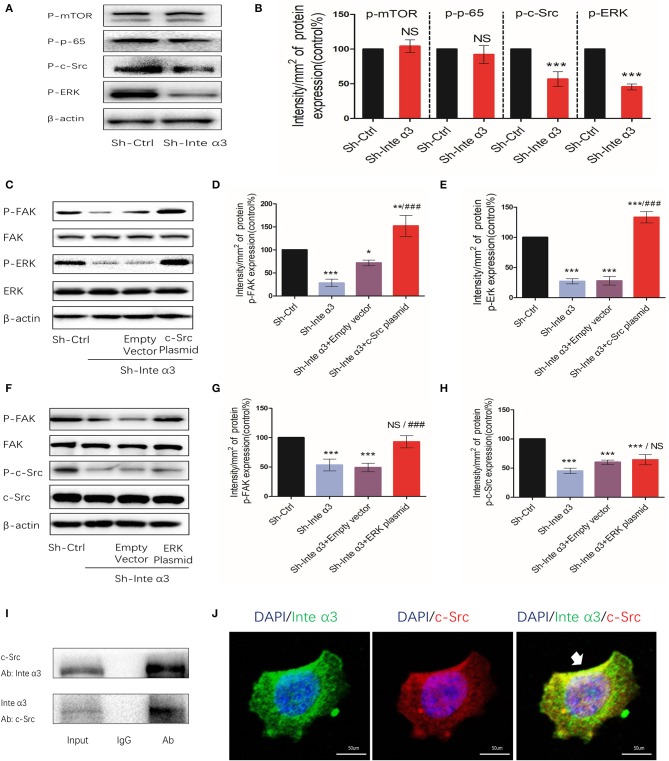
Figure 6.
Integrin α3 activates focal adhesion kinase (FAK) via the c-Src/extracellular signal-regulated protein kinase (ERK) signaling pathway. (A) Phosphorylated mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR), p-65, c-Src, and ERK were examined through western blotting in the Sh-Ctrl and Sh-Inte α groups; the corresponding quantification of the protein intensity is shown in (B). (C) The levels of phosphorylated FAK and ERK, as well as total FAK, ERK, and β-actin, were determined via western blotting among the Sh-Ctrl, Sh-Inte α3, Sh-Inte α3+empty vector, and Sh-Inte α3+c-Src plasmid groups; the corresponding quantification of p-FAK and p-c-Src protein intensity is presented in (D,E). (F) Among the Sh-Ctrl, Sh-Inte α3, Sh-Inte α3+empty vector, and Sh-Inte α3+ERK plasmid groups, the levels of phosphorylated FAK and c-Src, as well as total FAK, c-Src, and β-actin, were examined through western blotting; the quantification of p-FAK and p-ERK protein intensity is shown in (G,H). (I) Representative image of co-immunoprecipitation using anti-c-Src or anti-integrin α3, and subsequent detection of the other protein. (J) Representative immunofluorescence images showing colocalizations between integrin α3 and c-Src. Nuclei were stained with 4′-6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI) (blue), anti-c-Src linked to Alexa Fluor (red), anti-integrin α3 linked to fluorescein isothiocyanate (FITC) (green); original magnification: ×200. All experiments were repeated thrice with consistent results, and the representative images are shown. *P < 0.05 vs. control group; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001; ###P < 0.01.