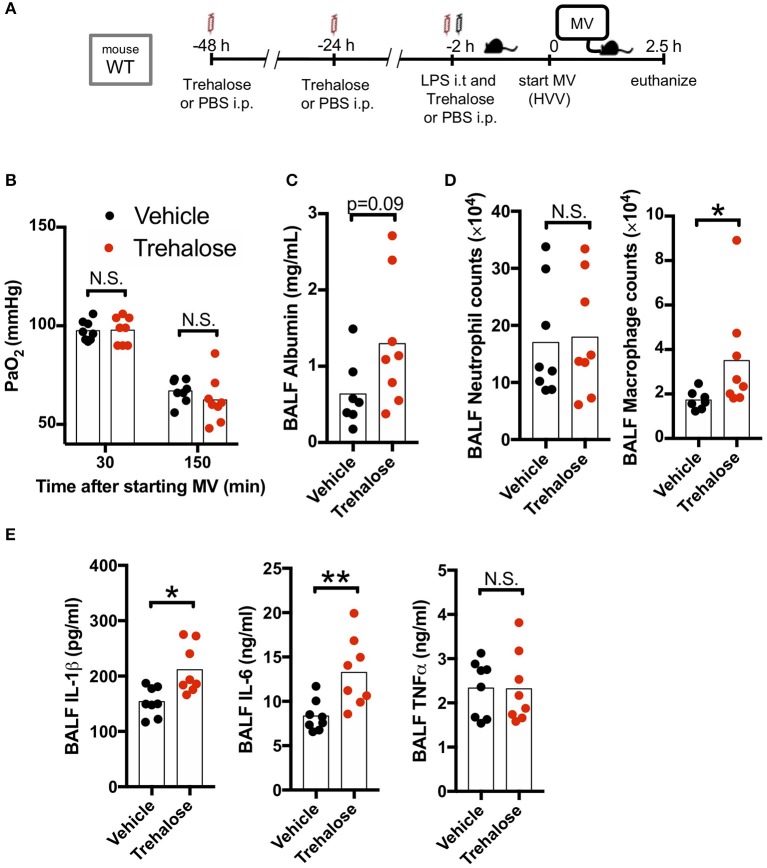
Figure 4.
Trehalose treatment does not rescue two-hit acute lung injury. (A) Study protocol. Forty eight, twenty four, and two hours before starting mechanical ventilation (MV), 1 g/kg of intraperitoneal trehalose or PBS was administered. Two hours before starting MV, 0.2 mg/kg i.t. LPS was administered. Then, mice were anesthetized and placed on high volume mechanical ventilation (HVV) with tidal volumes of 30 ml/kg with 3 cmH2O positive end-expiratory pressure (PEEP) for 2.5 h. (B) The effect of trehalose on arterial partial pressure of oxygen (PaO2). PaO2 was measured at 30 and 150 min after starting MV. No significance was detected in PaO2 between vehicle and trehalose groups by two-way ANOVA followed by Sidak's multiple comparisons test. (C) Lung permeability determined by albumin in BALF. (D) Absolute counts of neutrophils and macrophages in BALF. (E) Cytokine levels determined in BALF. (C–E) *,**indicates P < 0.05 and P < 0.01, respectively, determined by Mann-Whitney U-test. N.S., not significant.