Figure 1.
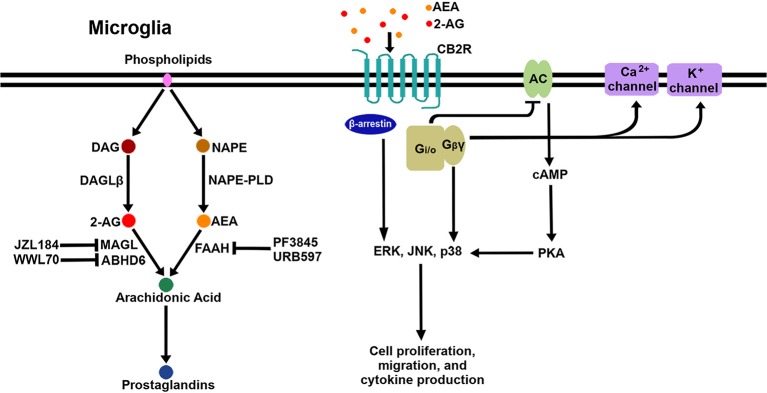
Schematic signaling pathways and biosynthesis/degradation of endocannabinoids in microglia. When eCB bind to CB2R on the microglial cell surface, the receptor initiates signaling through the canonical G-protein-dependent pathway and the non-canonical G-protein-independent pathway. Adenylyl cyclase (AC) is inhibited by the activation of Gi/o proteins; as a result, cAMP is reduced, followed by modulation of PKA signaling. Gβγ proteins activate certain calcium and potassium ion channels. Additionally, β-arrestin is recruited to CB2R to act as a receptor signal transducer or terminator. Three arms of the CB2R signaling pathway activate multiple downstream pathways, including several MAPKs (ERK, JNK, and p38 MAPK). AEA and 2-AG are mainly biosynthesized from NAPE by NAPE-PLD and from DAG by DAGLβ, respectively. AEA is degraded to arachidonic acid by FAAH, which is inhibited by PF3845 and URB597. 2-AG is degraded to arachidonic acid by MAGL and ABHD6, which are inhibited by JZL184 and WWL70, respectively. Arachidonic acid is a key precursor for prostaglandins.