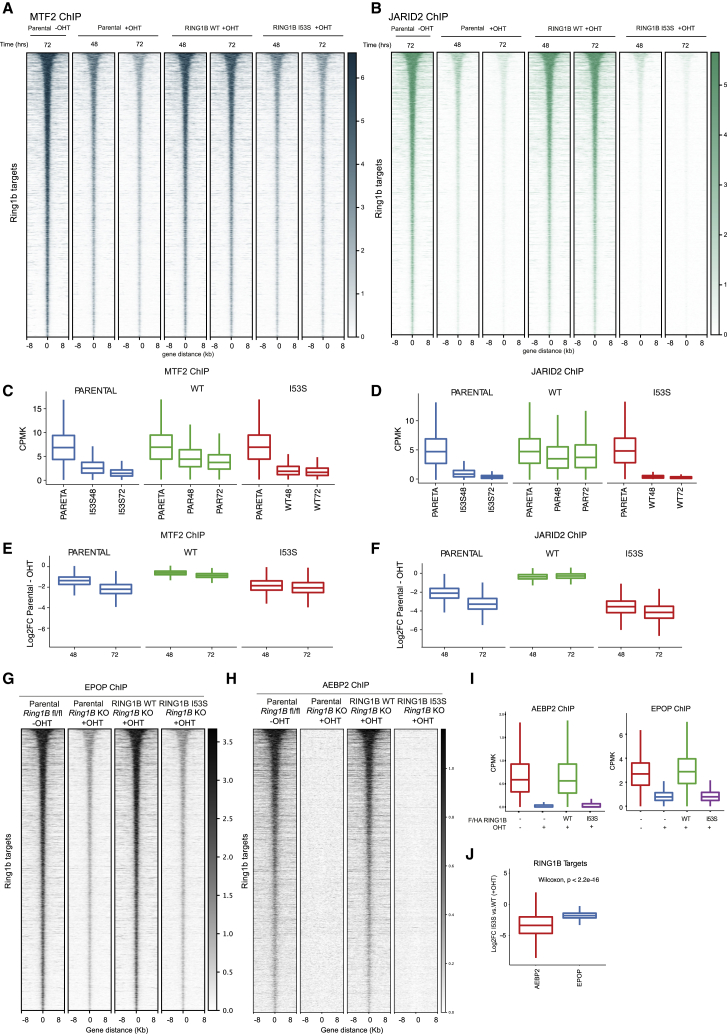
Figure 4.
H2AK119ub1 Loss Preferentially Abolishes PRC2.2 while Reducing PRC2.1 Chromatin Occupancy
(A) Heatmaps representing normalized MTF2 ChIP-seq intensities ±8 kb around the center of RING1B target loci in the indicated cell lines at the indicated time point post OHT induction.
(B) Heatmaps representing normalized JARID2 ChIP-seq intensities ±8 kb around the center of RING1B target loci in the indicated cell lines at the indicated time point post OHT induction.
(C) Boxplot representing MTF2 ChIP-seq CPMK levels in the indicated cell lines at RING1B target loci at the indicated time point post OHT induction.
(D) Boxplot representing JARID2 ChIP-seq CPMK levels in the indicated cell lines at RING1B target loci at the indicated time point post OHT induction.
(E) Boxplot representing the log2 ratio of MTF2 CPMK levels at RING1B target loci between RING1B WT- and I53S-expressing cells at the indicated time point post OHT induction.
(F) Boxplot representing the log2 ratio of JARID2 CPMK levels at RING1B target loci between RING1B WT- and I53S-expressing cells at the indicated time point post OHT induction.
(G) Heatmaps representing normalized EPOP ChIP-seq intensities ±8 kb around the center of RING1B target loci in the indicated cell lines.
(H) Heatmaps representing normalized AEBP2 ChIP-seq intensities ±8 kb around the center of RING1B target loci in the indicated cell lines.
(I) Boxplot representing AEBP2 (left) or EPOP (right) ChIP-seq CPMK levels in the indicated cell lines at RING1B target loci.
(J) Boxplot representing the log2 ratio of AEBP2 or EPOP CPMK levels at RING1B target loci between RING1B WT- and I53S-expressing cells.
See also Figures S1D and S1E.