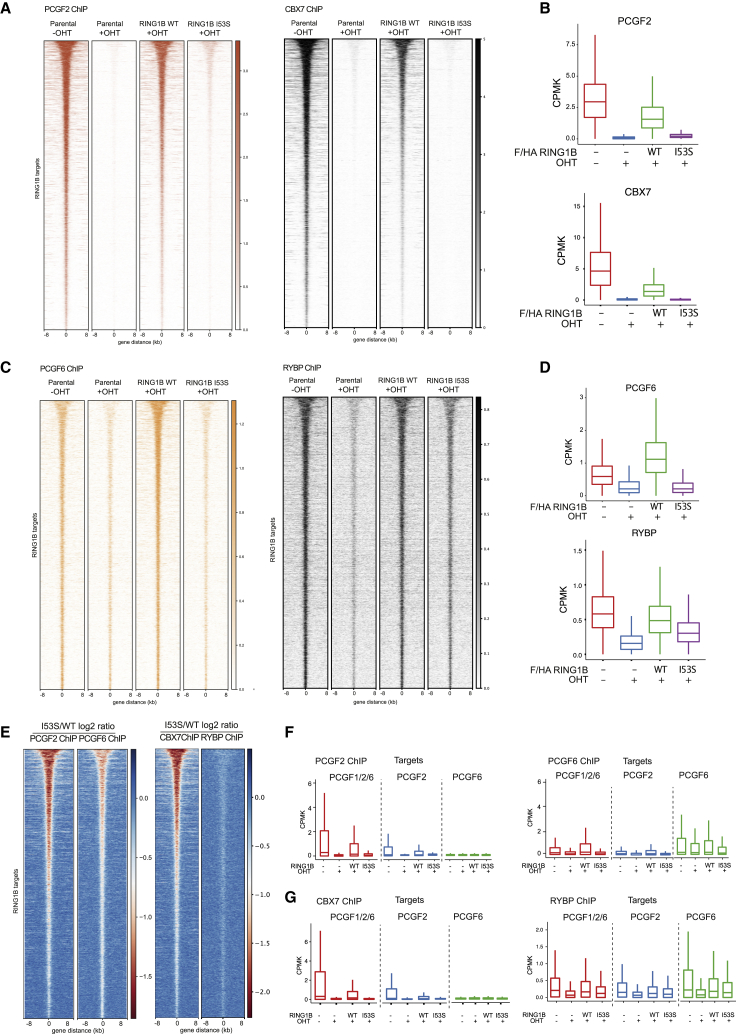
Figure 7.
RING1B Inactivation Preferentially Affects cPRC1
(A) Heatmaps representing normalized PCGF2 and CBX7 ChIP-seq intensities ±8 kb around the center of RING1B target loci in the indicated cell lines.
(B) Boxplots representing PCGF2 ChIP-seq CPMK levels (top panel) and CBX7 (bottom panel) in the indicated cell lines at RING1B target loci.
(C) Heatmaps representing normalized PCGF6 and RYBP ChIP-seq intensities ±8 kb around the center of RING1B target loci in the indicated cell lines.
(D) Boxplots representing PCGF6 ChIP-seq CPMK levels (top panel) and RYBP (bottom panel) in the indicated cell lines at RING1B target loci.
(E) Heatmap representing the log2 ratio of PCGF2 and PCGF6 (left) and CBX7 and RYBP (right) normalized ChIP-seq intensities at RING1B target loci between RING1B WT- and I53S-expressing cells.
(F) Boxplots representing PCGF2 (upper panel) and PCGF6 (bottom panel) ChIP-seq CPMK levels ±250 bp around TSS of PCGF target genes in the indicated cell lines.
(G) Boxplots representing CBX7 (left panel) and RYBP (right panel) ChIP-seq CPMK levels ±250 bp around TSS of PCGF target genes in the indicated cell lines.
See also Figures S2A–S2C.