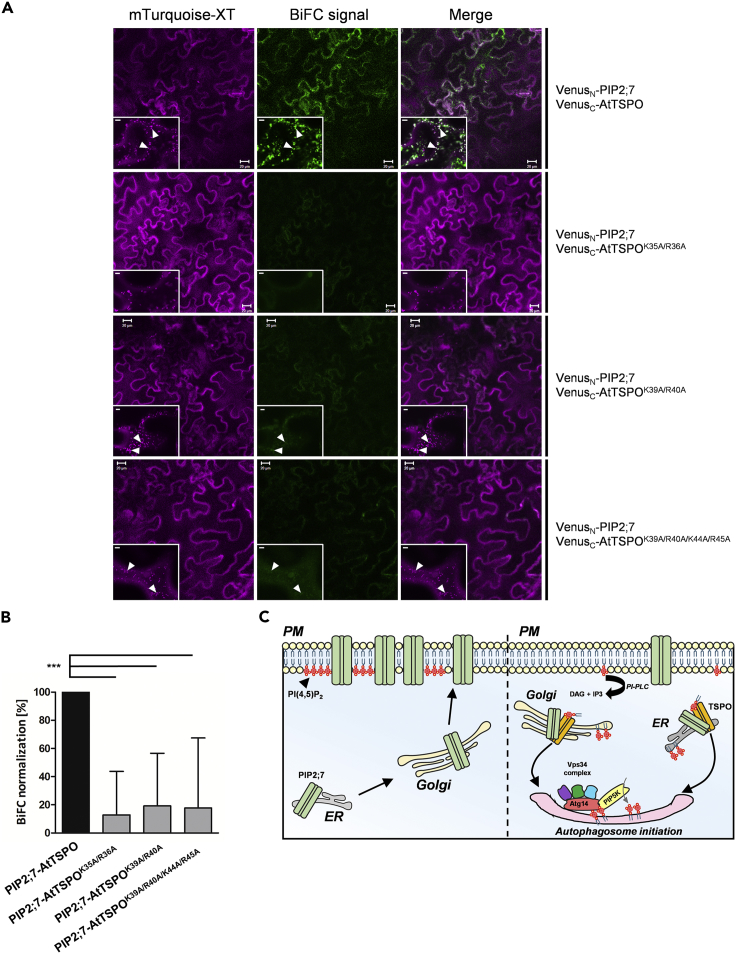
Figure 7.
Specific Positively Charged Lysine-Arginine Pairs in the N-terminal Region of AtTSPO Mediate Interaction with PIP2;7 In Vivo
(A) Representative confocal images of tobacco epidermal cells transiently coexpressing VenusN-PIP2;7 and VenusC-AtTSPO or VenusN-PIP2;7 and VenusC-AtTSPO point mutants. Xylosyltransferase-mTurquoise fluorescent chimera (magenta) served as a cell transfection control (Golgi marker) and for signal quantification. Full-length PIP2;7 and AtTSPO served as a positive control for the BiFC signal. Low-magnification images qualitatively demonstrate the occurrence and distribution of BiFC (green) in the transfected area, and insets of high-magnification images show Golgi stacks (arrowheads). For PIP2;7-AtTSPOK35A/R36A, colocalization of the BiFC signal and Golgi marker was not detected. Bars = 20 μm and 5 μm for low and high magnification, respectively. Experiments were repeated three times.
(B) Signal quantification showing a drastic reduction in BIFC between PIP2;7 and AtTSPO mutants compared with full-length AtTSPO. Statistical analysis was based on one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey's tests (***p < 0.001). Bars represent means +/− SD. See transparent methods section for quantification procedure.
(C) Hypothetical model of PI(4,5)P2-dependent PIP2;7 downregulation by AtTSPO during stress. Under normal conditions (left), synthesized PiP2;7 is targeted to the PM through the biosynthetic secretory pathway. Under osmotic stress conditions (right), expressed AtTSPO is targeted to the ER and Golgi membranes.AtTSPO stimulates PLC activity, depleting PI(4,5)P2 at the PM and generating DAG and PA that modulate the activity of PP2C phosphatases involved in ABA-dependent reduction of water loss through stomata. Decreased PI(4,5)P2 at the PM prevents recruitment of PIP2;7-containing vesicles. Golgi/ER-localized AtTSPO binds PI(4,5)P2 synthesized de novo in these compartments, inducing structural changes needed for recognition and interaction with PIP2;7 en route to the PM, causing redirection to nascent autophagosomes. AtTSPO cannot directly deplete PI(4,5)P2 from the PM but may form a protein complex that recruits PIP5K to organelle/autophagosome initiation sites. AtTSPO-mediated enrichment of ER/Golgi membranes with PI(4,5)P2 may initiate autophagy. Autophagosomal membranes also recruit PIP5K that generates PI(4,5)P2 and the autophagy regulator Atg14/Barkor that interacts with both the enzyme and PI(4,5)P2. PI(4,5)P2 binding to Atg14 regulates its interaction with the Vps34 complex catalyzing PI3P synthesis at autophagosome initiation sites. The presence of the AtTSPO-PI(4,5)P2-PIP2;7 complex in ER/Golgi membranes and the phagophore containing PI(4,5)P2 and Atg8 may be close enough to allow lipid-protein and protein-protein interactions.